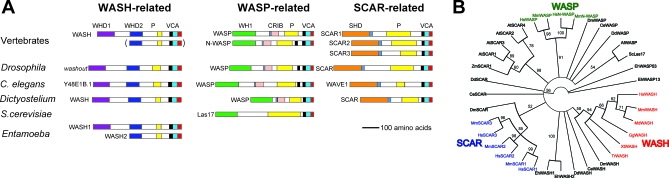
Figure 3. WASH Proteins Are Phylogenetically and Structurally Distinct from Known WASP Family Members.
(A) WASP family members and characteristic domains, adapted from reference [16] to show the new subfamily of WASH orthologs. Humans possess multiple WASH genes distributed in their subtelomeres, including short forms like one of two Entamoeba orthologs. Excluding Entamoeba, all other non-primate species examined have one WASH ortholog, except S. cerevisiae, in which there is only a WASP-related homolog. P, proline-rich domain; VCA, actin-binding and polymerizing domains; WHD1 and WHD2, subfamily-specific N-terminal domains of WASH (Figure S7).
(B) Neighbor joining tree of WASP family members based on C-terminal (VCA region) alignment (Figure S6). Bootstrap values were calculated over 1,000 iterations. Vertebrate clades with high bootstrap support are in color. Species are indicated using two-letter abbreviations in front of each protein name (see Text S1).