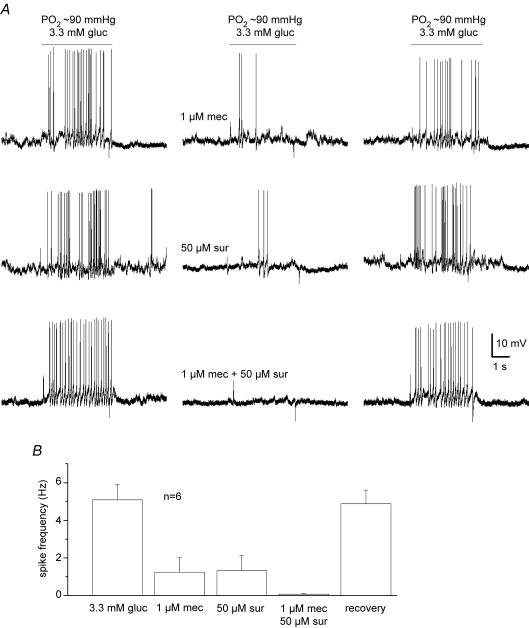
Figure 6.
Effects of nicotinic and purinergic receptor blockers on sensory discharge evoked by physiological hypoglycaemia in cocultures A, sample traces showing partial inhibition of sensory discharge induced by 3.3 mm glucose (PO2 ≈ 90 mmHg) in a cocultured petrosal neurone during exposure to the nicotinic blocker, mecamylamine (1 μm mec; upper traces) and the purinergic blocker, suramin (50 μm sur; middle traces). Note complete inhibition of sensory discharge by combined application of mecamylamine and suramin. Mean (± s.e.m.) spike frequency data for a group of 6 similar cocultured neurones before, during, and after application of the indicated receptor blockers are summarized in B.