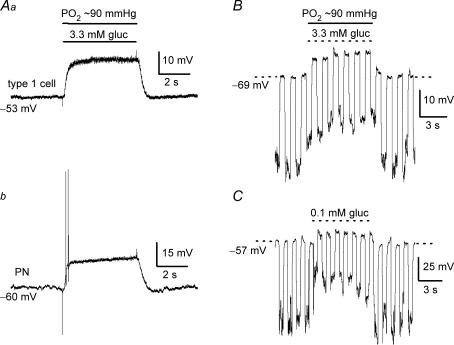
Figure 9.
Low glucose-induced receptor potential in type I cells and simultaneous recordings of presynaptic and postsynaptic chemoexcitatory responses in coculture Presynaptic depolarization or ‘receptor potential’ in a type I cell (Aa) and postsynaptic depolarization (and brief spike activity) in juxtaposed petrosal neurone (Ab) are shown during simultaneous paired recordings, before, during (horizontal bars) and after exposure of the coculture to physiological hypoglycaemia (3.3 mm glucose/PO2 ≈ 90 mmHg). The receptor potential was associated with a decrease in input resistance, as indicated by injecting constant hyperpolarizing current pulses (downward deflections), during application of 3.3 mm glucose (PO2 ≈ 90 mmHg) to a clustered type I cell (B) or 0.1 mm glucose (PO2 ≈ 140 mmHg) to a single type I cell ∼24 h after isolation (c).