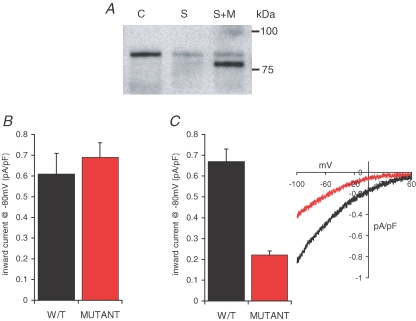
Figure 8.
Preventing constitutive STIM1 expression on the cell surface selectively inhibits ARC channel activity A, representative western blot showing the expression of the N-glycosylation mutant STIM1 protein levels in siRNA-transfected cells. Shown are STIM1 protein in control cells (C), in cells transfected with the STIM1 siRNA (S), and in siRNA-transfected cells expressing the siRNA-resistant N-glycosylation mutant STIM1 (S + M). Note that the glycosylation mutant runs at a lightly lower molecular mass, and that the siRNA-reduced endogenous STIM1 levels can be seen as a faint band in the same lane running at the normal molecular weight. B, the effects of the N-glycosylation mutant STIM1 on CRAC channel activity. Mean ±s.e.m. inward current density at −80 mV in siRNA-transfected cells expressing the siRNA-resistant wild-type STIM1 (black, n = 8) are compared with those in siRNA-transfected cells expressing the siRNA-resistant N-glycosylation mutant STIM1 (red, n = 7). C, the effects of the N-glycosylation mutant STIM1 on ARC channel activity. Mean ±s.e.m. inward current density at −80 mV (n = 6), and representative current–voltage relationship in siRNA-transfected cells expressing the siRNA-resistant wild-type STIM1 (black) are compared with those in siRNA-transfected cells expressing the siRNA-resistant N-glycosylation mutant STIM1 (red, n = 11).