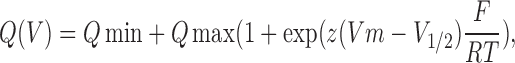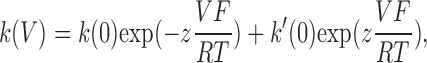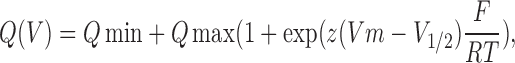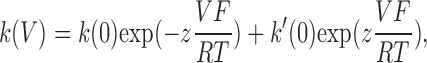The slow component of the ouabain-sensitive, presteady-state currents under Na
+/Na
+ exchange conditions was measured before and after exposure to MTSET in WT and mutant Na,K-ATPases. The panels on the left show the voltage dependence of the ouabain-sensitive presteady-state charge translocation (Q). The smooth curves correspond to the best fitting Boltzmann equation:
where
Q(
V) is the charge displacement produced by the voltage step,
Qmin the charge displaced at the maximum negative membrane potential,
Qmax the maximum displaceable charge during a negative to positive potential jump,
Vm the membrane potential,
V
1/2 the midpoint potential,
z the apparent valence, which was set to 1.
F,
R, and
T have their usual meanings. The panels on the right show the voltage dependence of the relaxation rate of the slow component of the ouabain-sensitive presteady-state currents. The smooth curves show the best fitting curves corresponding to the following equation:
which describes the voltage (
V) dependence of the relaxation rate constant
k as the sum of the forward and a backward voltage-sensitive rate constants with an effective charge
z and values of
k(0) and
k′(0) at 0 mV, respectively.
F,
R, and
T have their usual meanings. The curves with open symbols represent the measurements before MTSET perfusion, and those with the filled symbols represent the measurements after exposure to MTSET. The number of measurements was between four and eight. The mean values of
Q and
k, measured in WT before MTSET treatment (open symbols in the top plot), are shown as a thick dashed line (without symbols or error bars) in the plots for each mutant for comparison.