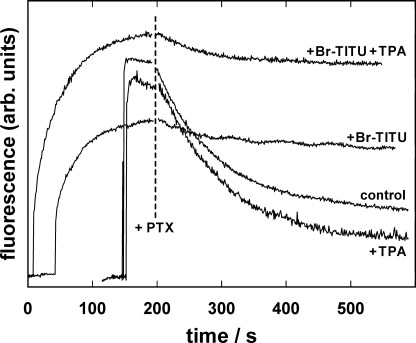
Figure 9.
Effect of access-channel blockers on the PTX-induced action of the Na,K-ATPase in the absence of monovalent cations other than H+. Na,K-ATPase was phosphorylated in standard buffer by 0.5 mM Tris phosphate in the absence or presence of 15 μM Br2-Titu3+ and/or 30 mM TPA+. After reaching a steady-state level of the fluorescence, corresponding to state P-E2, 150 nM PTX was added. Only Br2-Titu3+, the blocker of the cytoplasmic access channel, produced a striking difference by reducing the amplitude of the fluorescence decrease by about a factor of five. TPA+ had no significant effect. In all four cases, the rate constant of the exponential decay was 0.01 ± 0.0002 s−1.