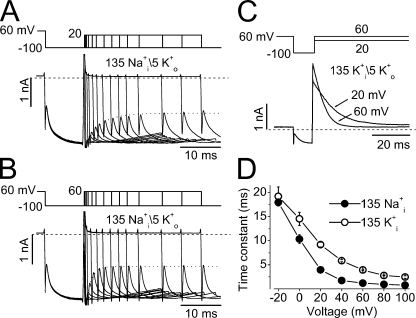
Figure 6.
Voltage-dependent inactivation of hERG channels in the presence of 135 Na+ i (A, B, and D) or 135 mM K+ i (C and D). (A and B) hERG currents evoked by the voltage protocol shown above the traces to monitor the time-dependent channel inactivation at 20 (A) or 60 mV (B). hERG channels were inactivated at the holding potential of 60 mV. Repolarization to −100 mV (P1) caused channel recovery from inactivation. The membrane was depolarized to 20 or 60 mV with increasing durations (P2) to induce the voltage-dependent inactivation, which was judged by the instantaneous currents upon repolarization to −100 mV (P3) after P2. The instantaneous currents immediately after the cell capacitive current upon P3 were fitted to the single exponential function (dotted lines) to obtain the inactivation time constants. (C) Inactivation time courses of the hERG outward K+ current at 20 or 60 mV. hERG channels were inactivated at the holding potential of 60 mV. Repolarization to −100 mV induced channel recovery from inactivation. The membrane was then depolarized to 20 or 60 mV to induce current inactivation, which was fitted to a single exponential function. (D) Inactivation time constant–voltage relationships of hERG channels under 135 Na+ i/5 mM K+ o (•, n = 5) or 135 mM K+ i/5 mM K+ o (◯, n = 4).