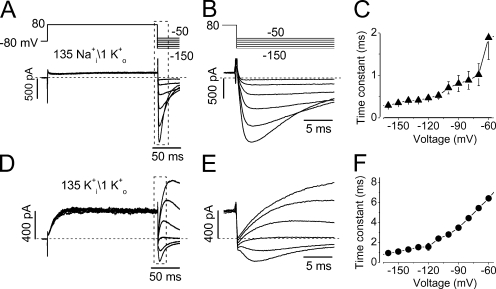
Figure 7.
Recovery from inactivation of hERG channels under conditions of 135 mM Na+ i/1 mM K+ o (A–C) or 135 mM K+ i/1 mM K+ o (D–F). hERG currents were recorded with a bath solution containing 1 mM K+ plus 135 mM NMG+ and a pipette solution containing either 135 mM Na+ (A–C) or 135 mM K+ (D–F). (A) hERG outward Na+ currents and the inward K+ currents elicited by the voltage protocol above the current traces. (B) The expansion of initial phase of the tail currents in A. The rising phase of the tail current upon repolarization reflects the fast recovery of the inactivated channels to the open state before deactivation. The rising phase of the tail current was fitted to a single exponential function to obtain the time constant of recovery from inactivation (τrec) at each voltage. (C) The τrec–voltage relationships under 135 mM Na+ i/1 mM K+ o (n = 6). (D) hERG outward and inward K+ currents elicited by the same voltage protocol shown at the top of A. (E) The expansion of initial phase of the tail currents in D. The rising phase of the tail current was fitted to a single exponential function to obtain the time constant of recovery from inactivation (τrec) at each voltage. (F) The τrec–voltage relationships under 135 mM K+ i/1 mM K+ o (n = 7).