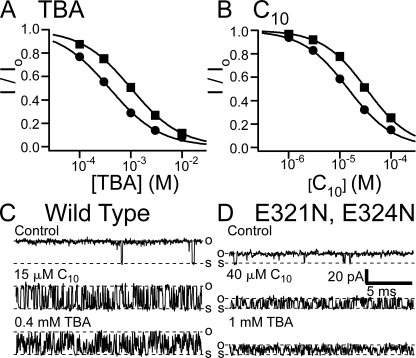
Figure 9.
Affinities and association rates for QA blockers are reduced in the E321N, E324N mutant. (A) Dose–response curves for TBA block of the E321N, E324N mutant (solid squares) and wild-type BK channels (solid circles). Remaining fractions of steady-state currents at 120 mV in the presence of different concentrations of TBA were determined from five patches for wild type and nine patches for the mutant. The average values and SEM are plotted as functions of TBA concentration. Smooth lines are fitted curves with Hill equation: I/Io= 1/(1 + ([TBA]/Kd)n). Values used in the fitting are Kd = 1.01 mM, n = 0.89 (mutant) and Kd = 0.38 mM, n = 0.87 (wild type). (B) Dose–response curves for C10 block of the E321N, E324N mutant (solid squares) and wild-type BK channels (solid circles). Remaining fractions of steady-state currents at 100 mV in the presence of different concentrations of C10 were determined from eight patches for the mutant and six patches for wild-type BK channels. The average values and SEM are plotted as functions of C10 concentration. Smooth lines are fitting curves of the data with Hill equation: I/Io= 1/(1 + ([C10]/Kd)n). Values used in the fitting are Kd = 32.8 μM, n = 1.01 (mutant) and Kd = 14.5 μM, n = 0.97 (wild type). (C) Single channel recordings of a wild-type BK channel at 120 mV in the absence (control) and presence of 15 μM C10 or 0.4 mM TBA. (D) Single channel recordings of an E321N, E324N channel at 120 mV in the absence (control) and presence of 40 μM C10 or 1 mM TBA.