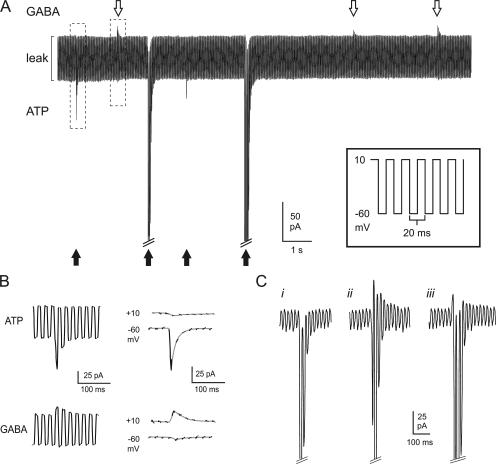
Figure 5.
Parallel monitoring of GABA and ATP release. (A, inset) Schematic of voltage protocol used to near-simultaneously resolve GABAergic and purinergic transient currents in cells infected with both GABAA and P2X2 receptors. The membrane potential was rapidly (50 Hz) alternated between ECl (−60 mV) and EP2X2 (+10 mV). (A) Sample recording showing ATP-induced inward currents (black arrows) and GABA-induced outward currents (white arrows) in a double-infected β-cell. Exocytosis was triggered by infusion of 0.2 μM free Ca2+ through the recording electrode. The largest inward currents have been truncated for display purposes. (B) Examples of an ATP-induced inward current and a GABA-induced outward response, marked by dashed boxes in A, shown on an expanded time base. In the right part, the current artifacts when switching between −60 and +10 mV have been removed and only current components at +10 and −60 mV are shown. The segments of the current recordings at the respective voltages have been connected by gray lines. (C) Examples of different types of events with a dominant inward current component: (i) inward current in isolation; (ii) clear out- and inward components; (iii) an outward component superseded by the activation of the inward current. The inward currents at −60 mV have been truncated for display purposes.