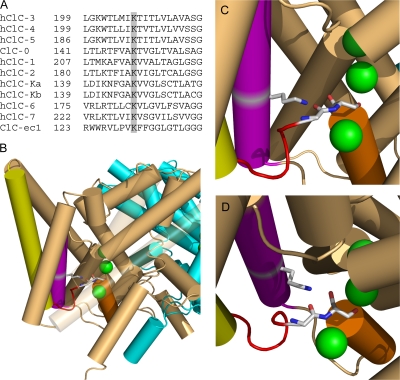
Figure 1.
K149 conservation and structure. (A) K149 is highly conserved. ClC-0 (Torpedo), ClC-ec1 (E. coli), and the nine human CLCs were aligned using Clustal-W. The alignment of helix E is shown with K149 and equivalent positions shaded. (B–D) K131 interacts with chloride-coordinating residues on loop CD. (B) Structure of ClC-ec1 (1OTT) as viewed from within the membrane with the extracellular space at the top. Three bound chloride ions (from top to bottom, bound to sites S ext, S cen, S int) are shown in green. Subunits A and B are shown in light brown and cyan, respectively. Selected secondary structures on subunit A are colored as follows: helix C, yellow; loop CD, red; helix D, orange; helix E, purple. Helixes J and M and loop LM are transparent. To illustrate the interaction between K149 (on helix E) and residues on loop CD, residues corresponding to K149 (K131), G122 (G106), and S123 (S107) (ClC-0 sequence numbers, with ClC-ec1 numbers in parentheses) are shown as sticks and in CPK coloring. (C) Close up of image in (B). (D) Image in C rotated to better show G106 and S107. In both C and D helixes J and M and loop LM are removed. Structural images were created using Pymol (DeLano, 2002).