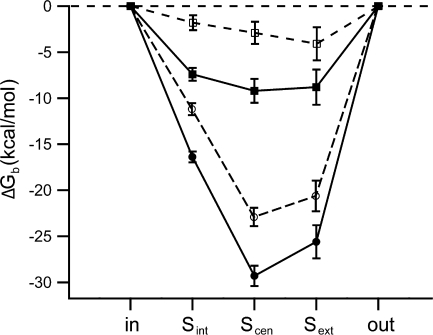
Figure 8.
Predicted effects of K149 mutants on chloride binding to ClC-0: homology model analysis. (A) Mutations at K149 decrease the affinity of chloride. Poisson-Boltzmann theory was used to calculate the electrostatic contribution to the free energy of chloride binding (ΔG b) to each site in the pore (starting from the cytoplasmic side: S int, S cen, S ext), for wild type (filled symbols, solid lines) and K149L (open symbols, dashed lines) ClC-0 homology models. The binding of the first chloride to the pore is shown in circles and the binding of the third chloride (two chlorides are already bound) is shown in squares. The methodology for structural modeling and electrostatics analysis is analogous to that previously reported (Engh et. al., 2007), except that here the side chain of E166 was neutralized and rotated away of the pore, so as to accommodate a chloride ion in S ext. A value of 4 was used as the dielectric constant of the protein (see supplemental material for further analysis). Lines connect data points for ease in viewing, and error bars represent an estimate of the discretization error arising from the grid-based Poisson-Boltzmann calculations.