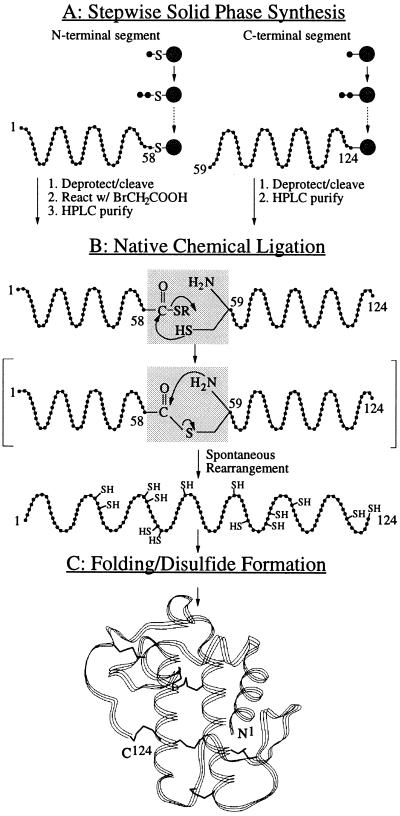
Figure 2.
Strategy for the total chemical synthesis of human sPLA2. (A) The 66-residue C-terminal segment of sPLA2 and the 58-residue N-terminal peptide-αCOSH segment were synthesized by stepwise SPPS techniques using Boc chemistry protocols, and the N-terminal thioacid peptide was activated by reaction with bromoacetic acid to form the peptide-αthioester. (B) Native chemical ligation of the two unprotected peptide segments results in formation of an amide bond at Gly58-Cys59. The two segments are initially joined by thioester formation (not observed as a discrete intermediate); subsequent spontaneous rapid rearrangement forms a native peptide bond at the ligation site (13). (C) Folding of the synthetic 124-residue polypeptide chain results in the formation of seven disulfide bonds and the generation of the active sPLA2 enzyme molecule.