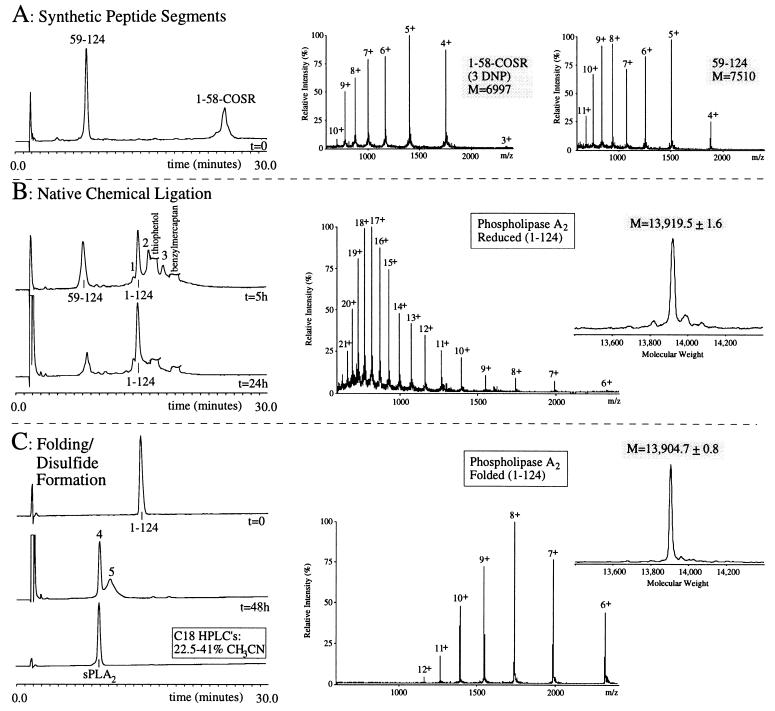
Figure 3.
Total synthesis of sPLA2 by native chemical ligation. (A) Reaction at t = 0. HPLC chromatogram of the starting synthetic peptide segments (Cys59-124) and (1-Gly58)-αCOSR, dissolved at 9 mg/ml in phosphate buffer (pH 7.5) containing 6 M GuHCl. ESMS spectra show the m/z ratios of the (1–58)-αCOSR peptide (3rd–10th ionized states) observed mass 6,996.5 ± 0.7 Da (calculated 6,997.7 Da, average isotope composition of the reduced peptide), and the (59–124)-peptide (4th–11th ionized states) observed mass of 7,510.1 ± 2.6 Da (calculated 7,510.6 Da, average isotope composition of the reduced peptide. (B) HPLC chromatograms of the ligation reaction, started by the addition of 1% thiophenol and 1% benzylmercaptan. At t = 5 hr (Upper), ligated product (1–124) is shown, as well as the C-terminal segment starting material. The unreacted N-terminal material can be accounted for as multiple intermediates eluting between 15 and 20 min (see text). Peak 1 represents a N-terminal peptide derivative; peaks 2 and 3 represent the ligated material (1–124) with, respectively, one and two DNP groups still attached to His side chains (see text). At t = 24 h (Lower), an almost quantitative ligation has occurred. The m/z pattern of the ligated material is shown (6th–21th ionized states) observed mass of 13,919.5 ± 1.6 Da (calculated 13,918.0 Da, average isotopic mass of the reduced peptide). (C) Folding and disulfide formation of the sPLA2 purified 124 residue polypeptide. HPLC chromatograms are shown of the purified reduced sPLA2 polypeptide (t = 0), the crude folded material (t = 48 hr), and the purified final product (sPLA2). The m/z pattern from the material in peak 4 is shown (6th–12th ionized state), observed molecular mass of 13,904.7 ± 0.8 Da (calculated 13,904.0 Da, average isotopic mass of the sPLA2 containing seven disulfides). Note the shift in m/z intensities between the reduced and folded sPLA2 (see text).