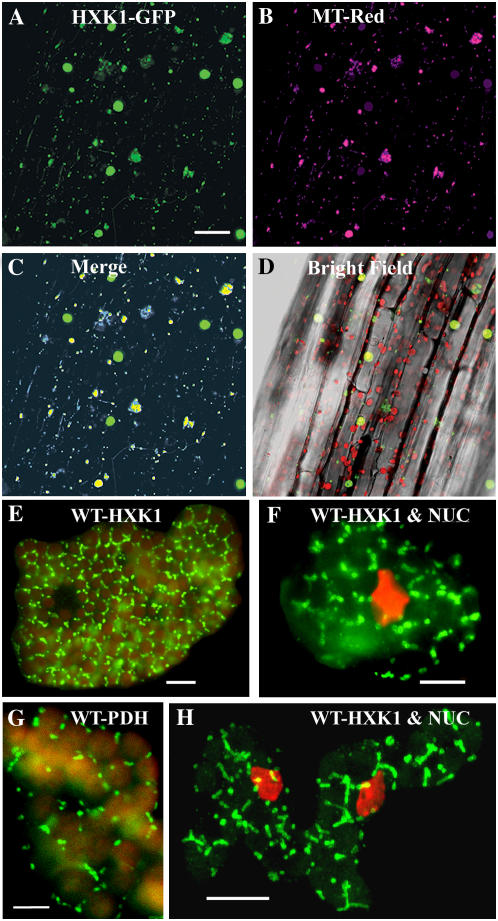
Figure 2.
Intracellular localization of Arabidopsis HXK1 in intact tissues. A to D, HXK1 localization in a seedling hypocotyl by fluorescence imaging of cauliflower mosaic virus 35S:HXK1-GFP expressed in Ler. Glc phosphorylation activity was increased about 18-fold in these seedlings (data not shown). A, Seedling hypocotyl showing punctate GFP fluorescence, occurring as smaller foci as well as larger aggregates. Scale bar = 50 μm. B, Seedling hypocotyl in A stained with MitoTracker Red and pseudocolored magenta. C, Merged images from A and B. Note codistributed blue-yellow fluorescence associated with the smaller foci and some larger foci. D, Hypocotyl images (A–C) merged with a corresponding bright-field image. Red shows Chl autofluorescence. E to H, Cellular immunolocalization of HXK in leaf mesophyll cells of young wild-type seedlings. Following cryofixation and freeze substitution, dissociated cells were labeled with anti-HXK1 polyclonal (E, F, and H) or anti-PDH monoclonal (G) antibodies, and then with secondary antibodies conjugated to FITC. Leaf cells were observed by fluorescence microscopy (E–G) or confocal microscopy (H); scale bars = 10 μm. H, Merged image of several optical sections and the rest (E–G) is each a single optical section. Staining of the nucleus (NUC) with DAPI is pseudocolored red (F and H). E and G, Red shows Chl autofluorescence.