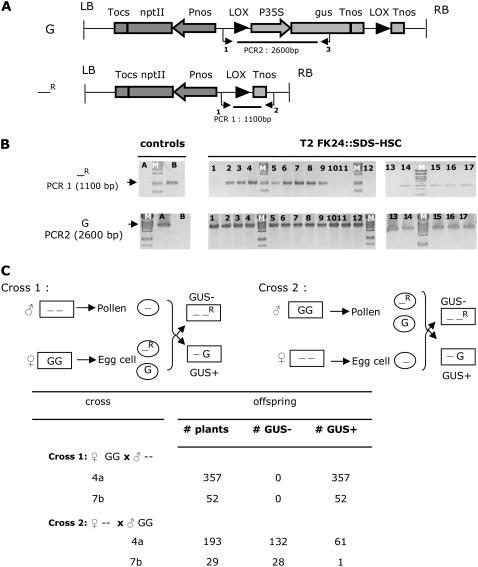
Figure 1.
Determining CRE functionality of the SDS promoter. A, Schematic presentation of the K2L610 T-DNA (De Buck et al., 1998) containing the p35S-gus chimeric gene, referred to as the gus allele (G) and the recombined allele (—R). The FK24 plant line is homozygous for a single-copy insertion of the K2L610 T-DNA. Primers used for PCR analysis are indicated below the constructs. B, PCR results on DNA purified from leaf material of T2 FK24∷SDS-HSC plants (lanes 1–17). Lane A, FK24; lane B, P35S-HSC; lane M, λ-DNA cut with PstI. PCR1, Primer LoxuitKP3 (primer 1) and primer Loxdel2 (primer 2); PCR2, primer LoxuitKP3 (primer 1) and primer GusR (primer 3). C, Reciprocal crossing scheme between a BAR-expressing plant and a homozygous T2 FK24∷SDS-HSC plant to determine in which germline the SDS promoter is functional. Boxed “--”: Genotype of the BAR expressing plant; −: absence of the nonrecombined and recombined allele; boxed “GG”: genotype of the T2 FK24∷SDS-HSC plant containing SDS-HSC; G: gus allele as presented in A; circled “-”: genotype of the gametes formed in the BAR-expressing plant; circled “G”: genotype of the gametes formed in the T2 FK24∷SDS-HSC when no recombination occurred in the respective germline; circled “-R”: genotype of gametes formed in the T2 FK24∷SDS-HSC when recombination occurred in the respective germline; boxed “--R”: recombined allele as presented in A. GUS+ and GUS−, Plants scored as GUS positive and GUS negative after GUS staining. Tnos, Polyadenylation signal of the nopaline synthase gene; Pnos, promoter of the nopaline synthase gene; nptII, neomycin phosphotransferase gene; P35S, CaMV 35S promoter; Tocs, polyadenylation signal of the octopine synthase gene; gus, gus gene.