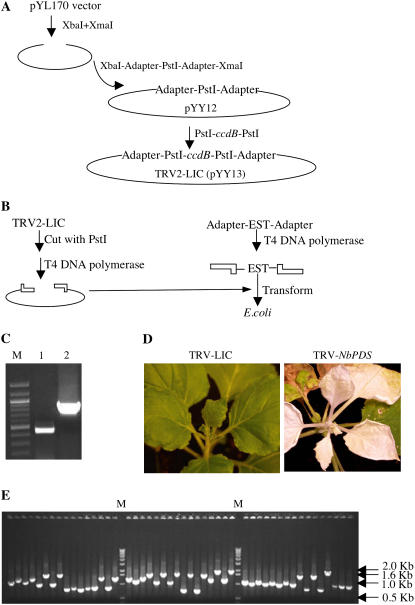
Figure 1.
TRV2-LIC vector. A, Construction of the TRV2-LIC vector. The TRV2 vector, pYL170, was used to generate the new TRV2-LIC vector by inserting a cassette containing adapters and two PstI sites in two digestion and ligation reactions. B, LIC cloning of inserts into TRV2-LIC. Briefly, the TRV2-LIC vector is digested with PstI and treated with T4 DNA polymerase. The EST carrying the relevant adapter sequences is generated by PCR and also treated with T4 DNA polymerase. The vector and insert are then mixed and used to transform Escherichia coli cells. C, TRV-LIC does not interfere with viral replication and spread as shown by the presence of TRV RNA1 (lane 1) and modified RNA2 (lane 2) in upper leaves of N. benthamiana plant. Lane M contains DNA size marker. D, TRV2-LIC allows efficient silencing of NbPDS as shown by the photobleaching of silenced plant (right). Control plant infiltrated with empty TRV-LIC vector shown for comparison (left). E, EST cloning efficiency into TRV-LIC is 100% as shown by PCR on colonies obtained from transformation with the vector and PCR product mixture. All 48 of the colonies tested here contain insert. Lane M contains DNA size marker.