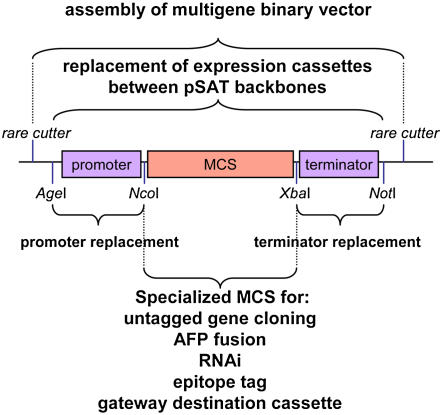
Figure 2.
The general structure of a pSAT-based plant expression vector. A typical vector is composed of promoter and terminator sequences, flanked by AgeI and NcoI and XbaI and NotI sites, respectively. This arrangement allows for easy replacement of these regulatory elements in nearly all of the pSAT-based vectors as well as the construction of various specialized tags and functional constructs between the NcoI and XbaI sites. Fully assembled expression cassettes can be mobilized between different pSAT backbones by AgeI-NotI and be cloned into pRCS-based vectors using various rare cutters. [See online article for color version of this figure.]