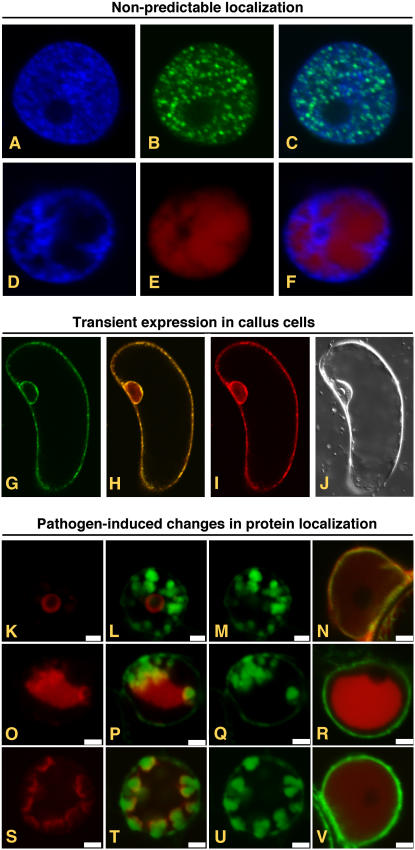
Figure 2.
Transient expression of AFPs from pSITE vectors. A to F, Expression of proteins whose subcellular localization cannot be determined in silico. Fluorescence from DAPI (A) and GFP (B) in the nucleus of a cell expressing a GFP:PYDV-P protein. The overlay of A and B is shown in C. Fluorescence from DAPI (D) and RFP (E) in the nucleus of a cell expressing a RFP:PYDV-N protein. The overlay of D and E is shown in F. Although both PYDV-N and -P proteins are entirely localized to the nucleus, analysis of their primary structure failed to identify karyophillic domains. G to J, Expression of AFP fusions in callus cells of N. benthamiana. G, GFP fluorescence of transgenic callus cell expressing mGFP5-ER. H, Overlay of G and I. I, RFP fluorescence following agromediated expression of RFP-SYNV-P from a pSITE vector. J, Differential interference contrast image of cell shown in G to I. K to V, Expression to study differential protein localization in pathogen-infected cells. Shown are confocal micrographs of RFP fusions of SYNV proteins expressed in SYNV-infected and mock-inoculated mGFP5-ER transgenic N. benthamiana plants. Fluorescence images for GFP, RFP, and the corresponding overlay are shown for each fusion expressed in SYNV-infected cells. Only the overlay is shown for fusions expressed in mock-inoculated leaves. Sections from top to bottom show localization of RFP:P (K–N), RFP:N (O–R), and RFP:M (S–V). Sections K to V are reprinted from Goodin et al. (2007).