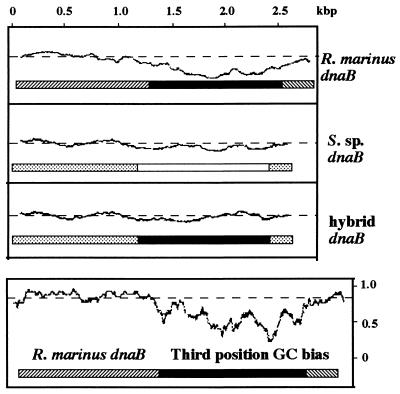
Figure 3.
Codon usage of the dnaB gene. (Upper) Pattern of codon usage determined by the technique of Gribskov et al. (32), using the GCG CodonPreference program with a window of 75 codons. Codon frequency tables used in the program were generated from 3 and 20 known genes for R. marinus and Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 (S. sp.), respectively. For each sequence, only the coding frame of the three possible reading frames is shown. Solid and open boxes correspond to intein coding regions of R. marinus dnaB and S. sp. dnaB, respectively. Hatched and stippled boxes correspond to extein coding regions of R. marinus dnaB and Synechocystis sp. dnaB, respectively. Hybrid dnaB is a hypothetical construct where the R. marinus DnaB intein is placed between Synechocystis sp. DnaB exteins and analyzed in the context of Synechocystis sp. genome. (Lower) Frequency of dG+dC present at the third position of each codon, which was determined using the CodonPreference program with a window of 25 codons. In each graph, codon usage typical of that organism scores close to the straight dashed line, as seen in the extein coding regions. Deviations from the norm result in troughs, which are readily apparent in the intein coding region of R. marinus dnaB.