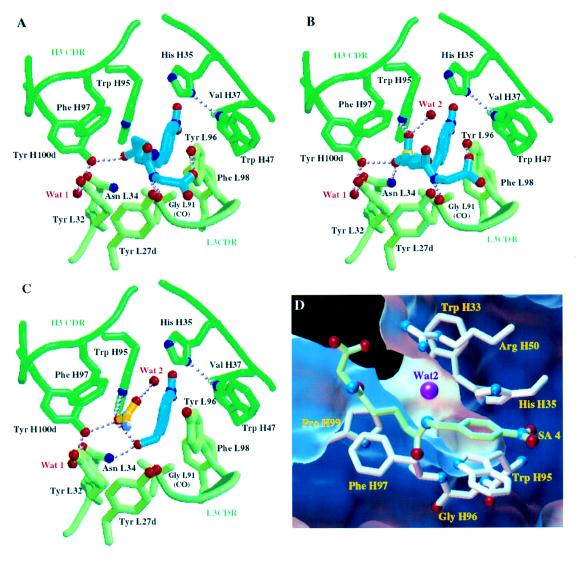
Figure 2.
Schematic views of D2.3 Fab residues that interact with the ligands examined. Residue numbering is according to ref. 24. In A–C, the ligands are in blue, the Cα trace of the Fab is in green, and water molecules are in red. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines. (A) Complex of D2.3 with amide 4, a stable SA. (B) Complex of D2.3 with TSA 3. (C) Complex of D2.3 with the reaction product 2, p-nitrobenzyl alcohol. Electron density corresponding to an acetate molecule was located in the combing site. The acetate is in yellow; the oxygens and the methyl of the acetate were distinguished on the basis of the hydrogen bonds established. A–C were drawn with molscript (25). (D) View of the canal (D2.3-4 structure) that allows water diffusion to the carbon atom of the carbonyl of 4 analogous to the reaction center in the complex of D2.3 with 1. The surface accessible to the exterior of a water molecule represented by a 1.4-Å radius sphere is cut to show the canal; its face toward the complexed Fab atoms is in blue, and the one facing the exterior is in white. Only the residues that border the canal are represented. Ligand 4 is in green; the water molecule (magenta) closest to the analogue of the reaction center is within hydrogen bonding distance and angle to Arg-H50 (hydrogen bond not shown). Nitrogen Nδ1 of His-H35 makes a hydrogen bond to Trp-H47 (not shown) that is conserved in antibodies; therefore, the Nɛ2 nitrogen of His-H35 (which is part of the canal’s wall) is protonated, and His-H35 most likely does not function as a general base in the hydrolysis catalyzed by D2.3. D was rendered in the avs environment (26).