Figure 4. Cdk5 is required for CASK recruitment to presynaptic terminals and for synapse formation.
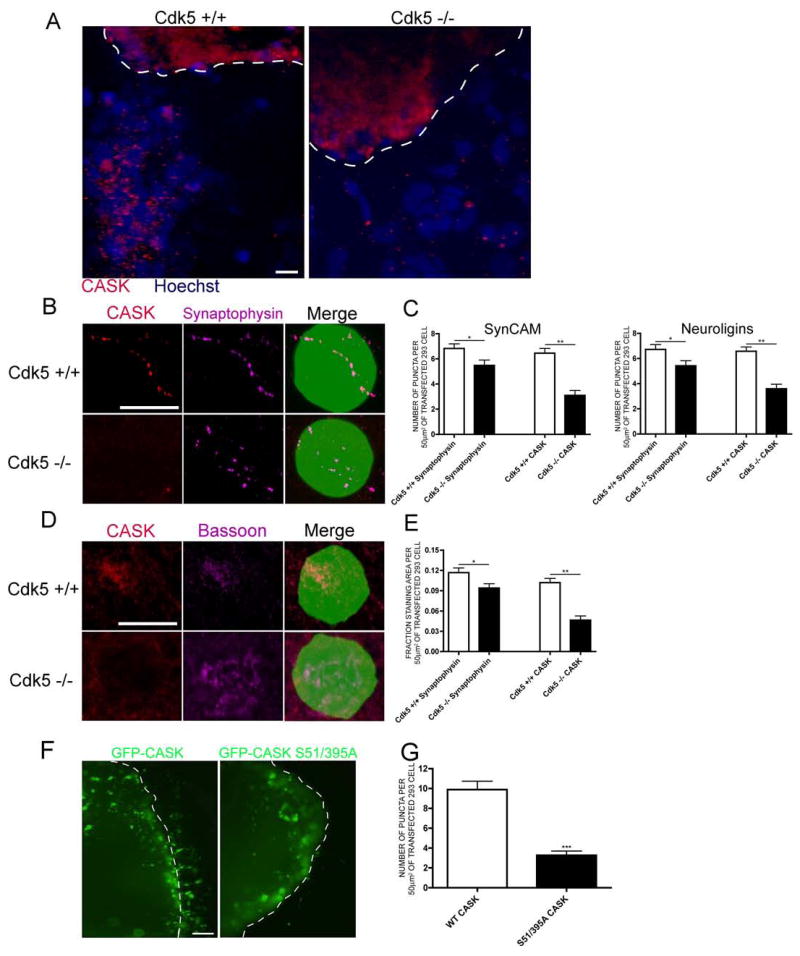
(a) Pontine explants from E17 wild-type or Cdk5-deficient mouse brains were cocultured with 293 cells expressing SynCAM isoforms. CASK staining is red and Hoechst nuclei are blue. The dashed white line indicates the border of the explant. Scale bar = 10 μm. (b) Pontine explants from E17 wild-type or Cdk5-deficient mouse brains were cocultured with 293 cells expressing SynCAM isoforms and GFP. CASK is red and Synaptophysin is purple. Scale bar = 10 μm. (c) One-Way ANOVA quantification of (b) for 293 cells expressing SynCAM or Neuroligin isoforms. * indicates p<0.05 and ** p<0.001. 40 cells were counted in 3 experiments. (d) Cortical neurons from E17 wild-type or Cdk5-deficient mouse brains were cocultured with 293 cells expressing SynCAM isoforms and GFP. CASK is red and Bassoon is purple. Scale bar = 10 μm. (e) One-Way ANOVA quantification of (d). * indicates p<0.05 and ** p<0.001. 40 cells were counted in 4 experiments. (f) Pontine explants were infected with HSV-GFP-CASK or CASK S51/395A prior to addition of transfected 293 cells. GFP is visualized in green. The dashed white line indicates the border of the explant. Scale bar = 5 μm. Comparison of puncta size with scale bar confirms these are not cell bodies migrating from the explant. (g) Student’s t-test quantification of (f). 40 cells were counted in n=6 experiments for wild-type and n=4 for mutant CASK. *** indicates p<0.0001.
