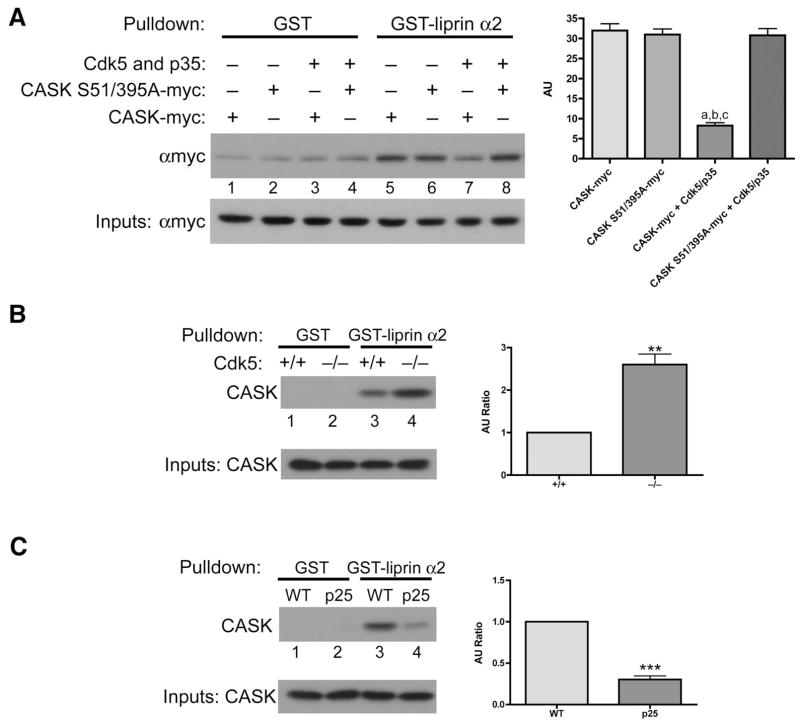
Figure 7. Cdk5 directly regulates the interaction between CASK and liprin-α.
(a) 293 cells were transfected with either CASK-myc or CASK S51/395A-myc alone or in combination with active Cdk5. Cell lysates were then subjected to GST pulldowns using a GST-liprin-α SAM domain fusion protein or GST control. Quantification of the pulldowns were carried out by densitometry with relative values being determined by subtraction of the background pulldown by GST (lanes 1–4) for each condition (lanes 5–8). One-Way ANOVA analysis was used. a, b and c indicate that p<0.001 when comparing lane 7 with lanes 5, 6 and 8, respectively and n=3. (b) Total forebrain lysates were made from wild-type or Cdk5-deficient littermates and subjected to GST pulldowns using a GST-liprin-α SAM domain fusion protein or GST control. Quantification was performed by assessing the densitometric signal and taking the ratio of CASK pulled down from Cdk5-deficient brains (in AU) relative to wild-type littermates (in AU). ** indicates p=0.0030 and n=3. (c) Total forebrain lysates were made from wild-type or CK-p25 littermates and subjected to GST pulldowns using a GST-liprin-α SAM domain fusion protein or GST control. *** indicates p<0.0001 and n=3.