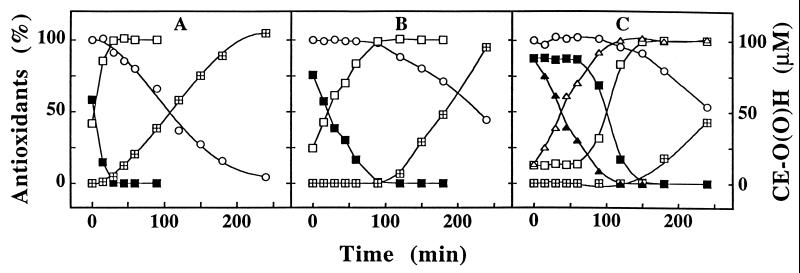
Figure 1.
Hydroquinones protect LDL’s cholesteryl esters from ROO⋅-induced peroxidation. An LDL solution (1.2 μM in apoB) was incubated at 37°C with 2 mM of AAPH in the absence (A) or presence (B) of 10 μM of 2,5-DTBHQ or α-TQH2 (C). At the time points indicated, aliquots were taken and analyzed for CoQ10H2 (▪), CoQ10 (□), α-TOH (○), and CE-O(O)H (⊞) and, where applicable, for α-TQH2 (▴) and α-TQ (▵). The data shown represent mean values of three separate experiments with a variation of <15%. The initial concentrations of CoQ10H2, CoQ10, and α-TOH in the LDL solution were 0.73 ± 0.15, 0.43 ± 0.09, and 9.5 ± 0.9 μM, respectively. The initial levels of α-TQH2 and α-TQ measured after addition of the freshly prepared hydroquinone to LDL varied between 8.9 to 9.1 and 1.1 to 1.6 μM, respectively. Note that the sum of CoQ10H2 plus CoQ10 and that of α-TQH2 plus α-TQ represent 100%.