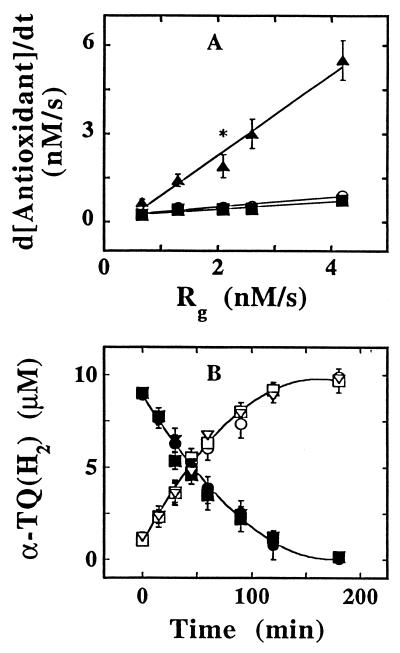
Figure 2.
The consumption of α-TQH2 during LDL oxidation is dependent on the rate of ROO⋅ production but independent of the α-TOH content of the lipoprotein. (A) LDL (1 μM in apoB), control or supplemented with 10 μM α-TQH2, was oxidized with increasing concentrations of AAPH, and the rates of consumption of CoQ10H2 (▪) and α-TOH (○) in the control and α-TQH2 (▴) in the supplemented LDL estimated from the linear portion of their respective depletion curves. Rg was calculated from Rg = 1.3 × 10−3 [AAPH] nM/s (34). The data shown are average values obtained from two or three (indicated by asterisk) independent experiments, with the range indicated by the vertical lines. (B) LDL (1.5 μM in apoB) from a FIVE patient depleted (circles), partially (squares), or fully re-supplemented with α-TOH (triangles) was incubated with 1 mM AAPH in the presence of 10 μM of α-TQH2. At the time points indicated, an aliquot was taken and analyzed for α-TQH2 (solid symbols) and α-TQ (open symbols). The data shown are mean values ± SD of three independent experiments performed with LDL prepared from plasma of one FIVE patient.