Abstract
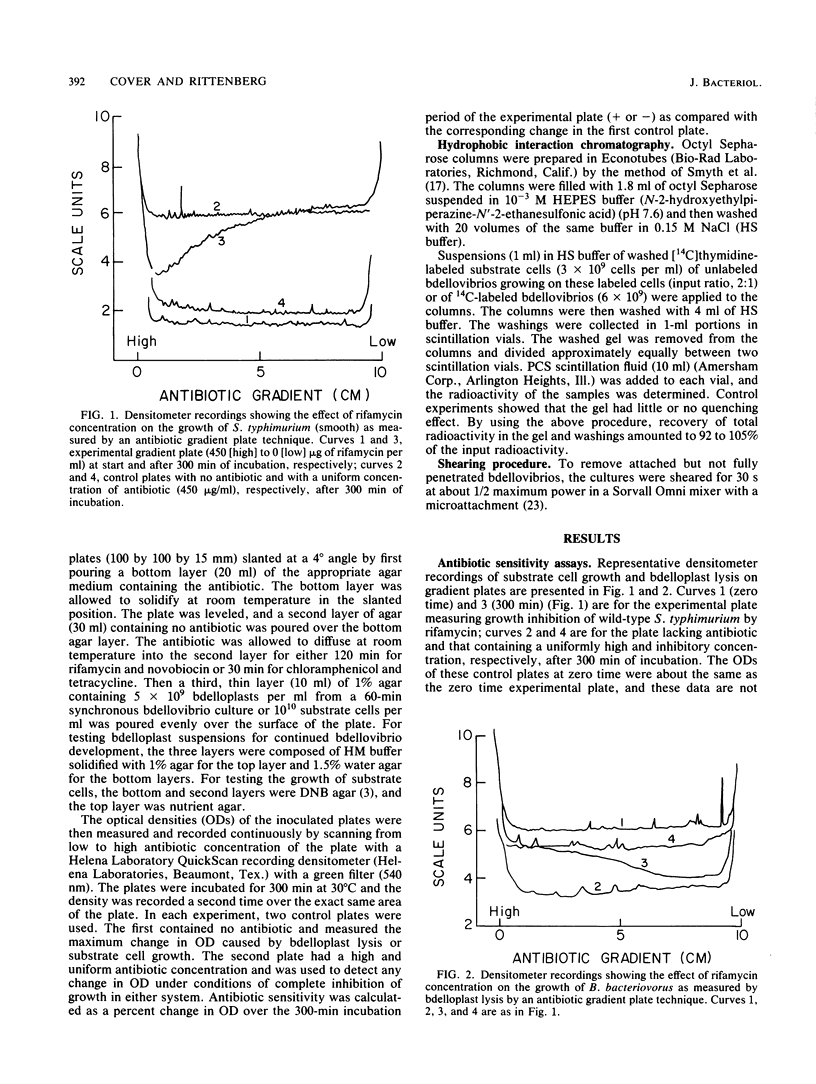
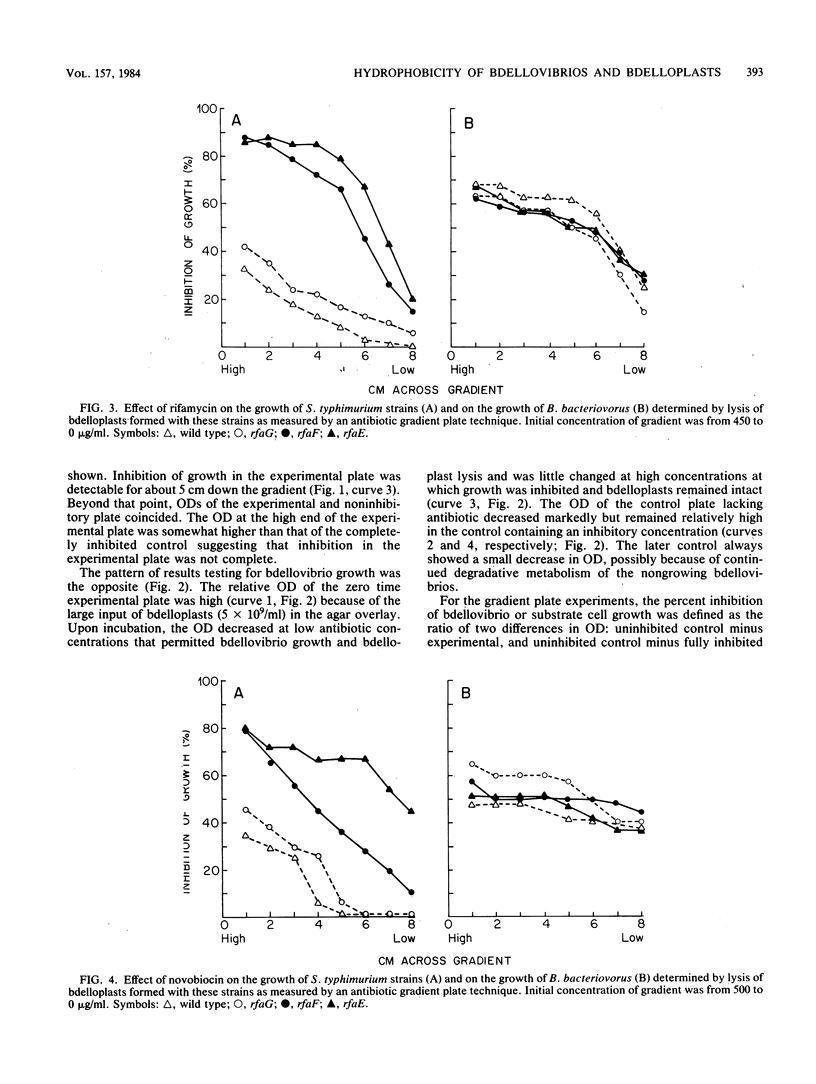
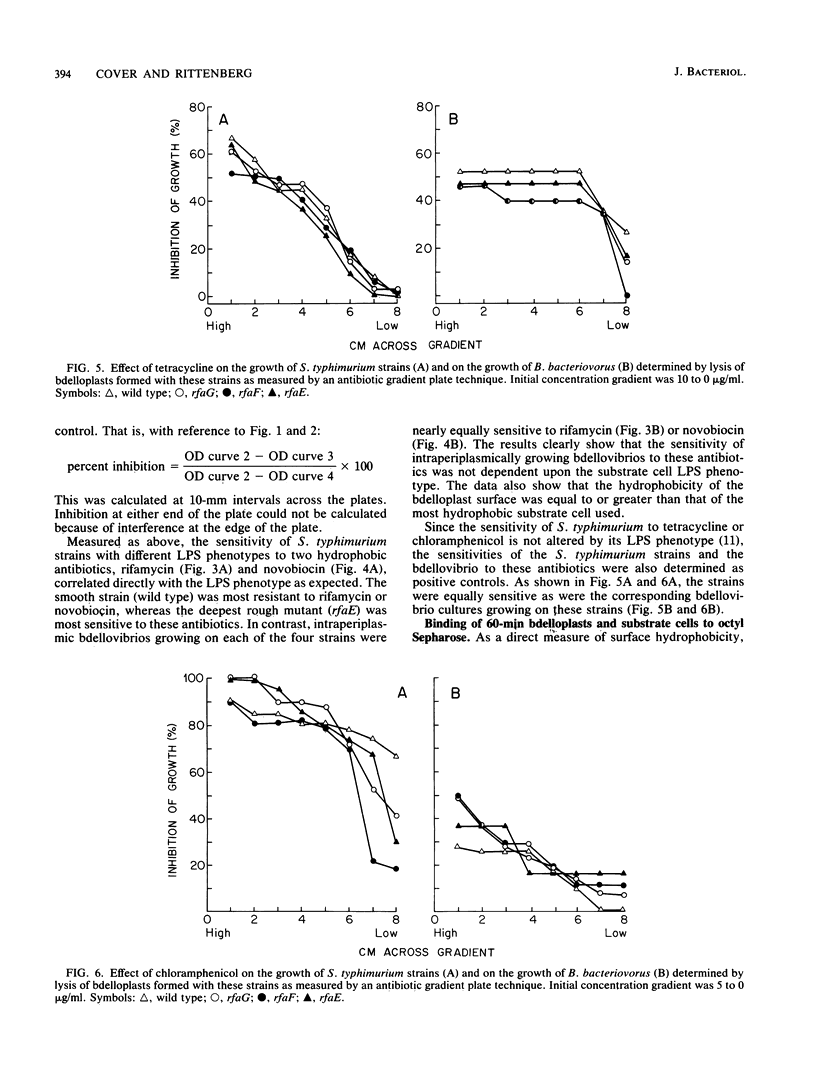
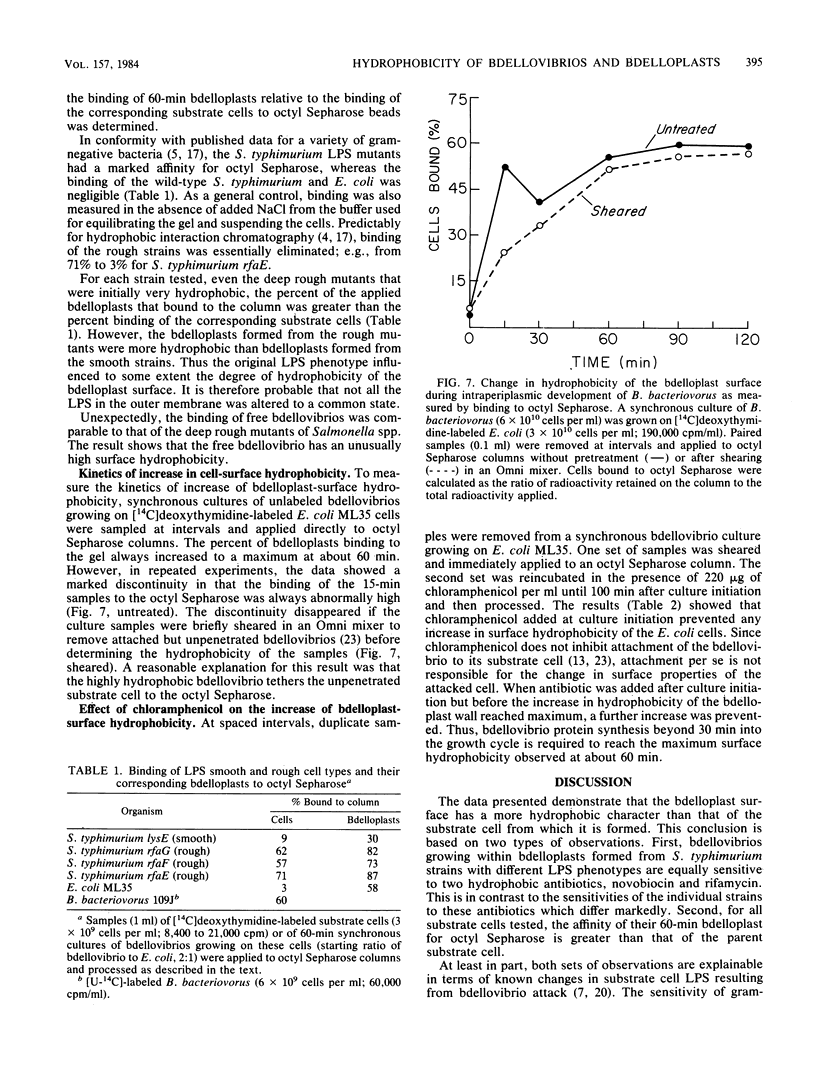
During intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J, the substrate cell surface becomes more hydrophobic. This was shown (i) by comparing the sensitivity to hydrophobic antibiotics of wild-type and lipopolysaccharide mutant strains of Salmonella typhimurium to that of the bdellovibrio growing on these strains and (ii) by measuring the binding efficiency of these strains, Escherichia coli, and their derived bdelloplasts to octyl Sepharose. The kinetics of increase in surface hydrophobicity was similar to the kinetics of the conversion of the substrate cell peptidoglycan to a lysozyme-resistant form (M. Thomashow and S. Rittenberg, J. Bacteriol. 135:1008-1014, 1978), and hydrophobicity reached a maximum at about 60 min in a synchronous culture. The change in hydrophobicity was inhibited by chloramphenicol, suggesting that bdellovibrio protein synthesis was required. Control experiments revealed that the free-swimming bdellovibrio had a more hydrophobic surface than the deep rough mutants of S. typhimurium.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abram D., Castro e Melo J., Chou D. Penetration of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus into host cells. J Bacteriol. 1974 May;118(2):663–680. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.2.663-680.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Spudich E. N., Nikaido H. Protein composition of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: effect of lipopolysaccharide mutations. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):406–416. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.406-416.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cover W. H., Martinez R. J., Rittenberg S. C. Permeability of the boundary layers of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J and its bdelloplasts to small hydrophilic molecules. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):385–390. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.385-390.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Davies J., Grundström T., Kihlström E., Normark S. Surface charge and hydrophobicity of Salmonella, E. coli, Gonococci in relation to their tendency to associate with animal cells. Scand J Infect Dis Suppl. 1980;Suppl 24:135–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson K. E., Stendahl O., Tagesson C., Edebo L., Johansson G. The tendency of smooth and rough Salmonella typhimurium bacteria and lipopolysaccharide to hydrophobic and ionic interaction, as studied in aqueous polymer two-phase systems. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B. 1977 Jun;85(3):212–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1977.tb01698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Rittenberg S. C. Incorporation of substrate cell lipid A components into the lipopolysaccharide of intraperiplasmically grown Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):860–868. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.860-868.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Rittenberg S. C. Partial characterization of lipid A of intraperiplasmically grown Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):869–874. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.869-874.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C., Hespell R. B. Energy efficiency of intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):1158–1165. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.1158-1165.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenberg S. C., Shilo M. Early host damage in the infection cycle of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1970 Apr;102(1):149–160. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.1.149-160.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roantree R. J., Kuo T. T., MacPhee D. G. The effect of defined lipopolysaccharide core defects upon antibiotic resistances of Salmonella typhimurium. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Dec;103(2):223–234. doi: 10.1099/00221287-103-2-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosson R. A., Rittenberg S. C. Regulated breakdown of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid during intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):620–633. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.620-633.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZYBALSKI W., BRYSON V. Genetic studies on microbial cross resistance to toxic agents. I. Cross resistance of Escherichia coli to fifteen antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1952 Oct;64(4):489–499. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.4.489-499.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlecht S., Schmidt G. Möglichkeiten zur Differenzierung von Salmonella-R-Formen mittels Antibiotica und antibakterieller Farbstoffe. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970;212(2):505–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlecht S., Westphal O. Untersuchungen zur Typisierung von Salmonella-R-Formen. 4. Typisierung von S. minnesota-R-Mutanten mittels Antibiotica. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1970 Apr;213(3):356–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit J., Kamio Y., Nikaido H. Outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium: chemical analysis and freeze-fracture studies with lipopolysaccharide mutants. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):942–958. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.942-958.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smyth C. J., Jonsson P., Olsson E., Soderlind O., Rosengren J., Hjertén S., Wadström T. Differences in hydrophobic surface characteristics of porcine enteropathogenic Escherichia coli with or without K88 antigen as revealed by hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Infect Immun. 1978 Nov;22(2):462–472. doi: 10.1128/iai.22.2.462-472.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snellen J. E., Starr M. P. Alterations in the cell wall of Spirillum serpens VHL early in its association with Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109D. Arch Microbiol. 1976 May 3;108(1):55–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00425093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J: N-deacetylation of Escherichia coli peptidoglycan amino sugars. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1008–1014. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1008-1014.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J: attachment of long-chain fatty acids to escherichia coli peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):1015–1023. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.1015-1023.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Rittenberg S. C. Intraperiplasmic growth of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus 109J: solubilization of Escherichia coli peptidoglycan. J Bacteriol. 1978 Sep;135(3):998–1007. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.3.998-1007.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varon M., Shil M. Interacton of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus and host bacteria. I. Kinetic studies of attachment and invasion of Escherichia coli B by Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):744–753. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.744-753.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


