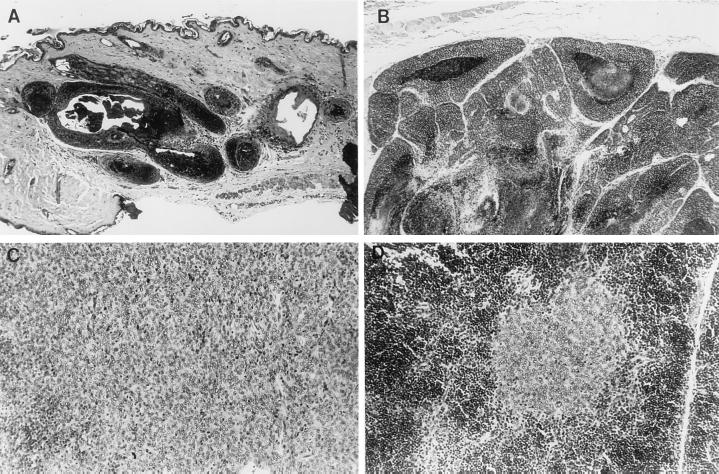
Figure 3.
Microscopic sections of tumors induced by wild-type and mutant polyoma strains. (A) Hair follicle tumors induced by wild-type polyoma virus. These tumors typically grow to only several times the diameter of a normal hair follicle (×90). (B) Hair follicle tumor induced by polyoma mutant 250YS. At this magnification (×90) only part of the tumor is seen. (C) A portion of a thymic epithelioma induced by wild-type polyoma virus. These tumors grow to sizes upwards of 2 cm in diameter (× 180). (D) Thymic epithelioma induced by polyoma mutant 250YS. The tumor is histologically identical to the wild-type tumor (C) but relatively very small (×180).