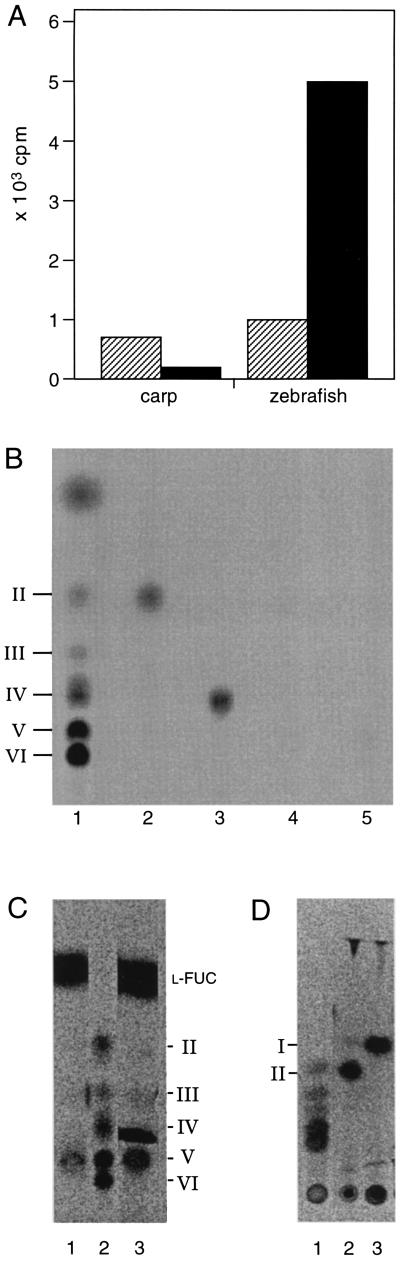
Figure 1.
Radiolabeling of gastrulation-specific metabolites. Extracts of zebrafish or carp embryos from the gastrulation stage were incubated in the presence of radiolabeled or unlabeled UDP-GlcNAc (see Materials and Methods). (A) Incorporation of UDP-[U14C]GlcNAc into HPLC fractions with retention times similar to chitin tetraose (striped box) and chitin pentaose (filled box). In the incubations where unlabeled UDP-GlcNAc was used, the equivalent fractions were incubated with the NodZ protein in the presence of GDP-[U-14C]fucose. By using this assay it is possible to specifically detect chitin oligosaccharides at concentrations as low as 1 picomol (data not shown). The pooled fractions were used for chitinase and chitobiase treatments and separated on TLC (B–D). (B) Radiolabeling of metabolites obtained from carp embryos and separated by HPLC, using the NodZ transfucosylation assay. Lanes: 1, fucosylated chitin oligosaccharide standards (as described in ref. 4); 2 and 3, HPLC fractions with retention times similar to chitin tetraose after transfucosylation, incubated with chitinase (lane 2) or without chitinase (lane 3); 4 and 5, HPLC fractions with retention times similar to chitin pentaose after transfucosylation, incubated with chitinase (lane 4) or without chitinase (lane 5). (C and D) Radiolabeling of metabolites obtained from zebrafish embryos using the NodZ transfucosylation assay. Fucosylated chitin oligosaccharide standards (C, lane 2; and D, lane 1); HPLC fractions with retention times similar to chitin pentaose after transfucosylation {C, lanes 1 and 3 (without removing free GDP-[U-14C]fucose)} incubated with chitinase (D, lane 2), or incubated with chitinase and chitobiase (from Streptomyces griseus, Sigma) (D, lane 3).