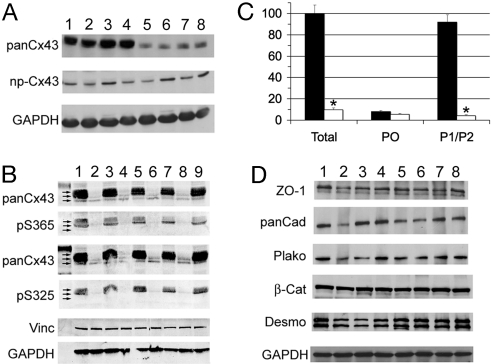
Fig. 3.
Aberrant expression of Cx43 in ODDD mutant hearts. (A) Western blot analysis of wild-type (WT) and ODDD mutant (ODDD) hearts using rabbit antibody 18B, which reacts with all forms of Cx43 (panCx43) and mouse monoclonal CX1B1, which preferentially reacts with the P0 form of Cx43 (np-Cx43). Lanes 1–4 are from wild-type hearts, and lanes 5–8 are from ODDD hearts. Signals were visualized with enhanced chemiluminescence. (B) Western blot analysis using mouse monoclonal Cx43NT1, which recognizes all forms of Cx43, and rabbit anti-pS325/328/330-Cx43 and rabbit anti-pS365-Cx43 antibodies, which recognize specific phosphorylated forms of Cx43. Lanes 1, 3, 5, 7, and 9 are from wild-type hearts, and lanes 2, 4, 6, and 8 are from ODDD hearts. Equivalency of loading was verified by probing for vinculin (vinc) and GAPDH. Signals were visualized and quantified using the Li-Cor imaging system. Arrows in A and B indicate P0, P1, and P2 forms of Cx43. (C) Abundance of total Cx43, P0, and P1/P2 forms of Cx43 in wild-type (■) and ODDD (□) hearts. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM relative to total Cx43 levels in wild-type hearts. (D) Western blot analysis for zona occludens-1 (ZO-1), pan-cadherin (panCad), plakoglobin (plako), β-catenin (β-Cat), desmoplakin (desmo), and GAPDH. Lanes 1–4 are from wild-type hearts, and lanes 5–8 are from ODDD hearts.