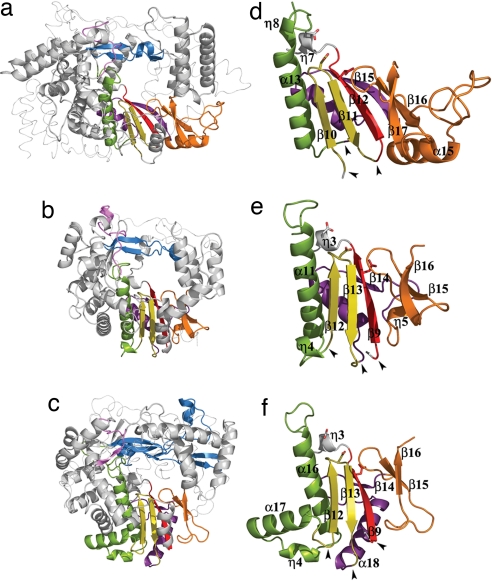
Fig. 2.
The conserved structural polymerase motifs. (a–c) The polymerase core of IBDV VP1 (a) compared with the equivalent cores in FMDV (b) and bacteriophage φ6 (c) RDRPs. The secondary structural elements containing the conserved motifs are colored as follows: A, red; B, green; C, yellow; D, purple; E, orange; F, blue; G, pink. The N- and C-terminal domains are shown as thin ribbons. (d–e) Structural organization of the permuted palm subdomain of IBDV VP1 (d) compared with the canonical palm subdomains of FMDV (e) and φ6 (f) RDRPs. Side chains of the acidic residues in the polymerase catalytic sites are shown as sticks. The black arrowheads indicate positions where the backbone connectivity is broken in the canonical polymerases and reconnected in the permuted IBDV RDRP.