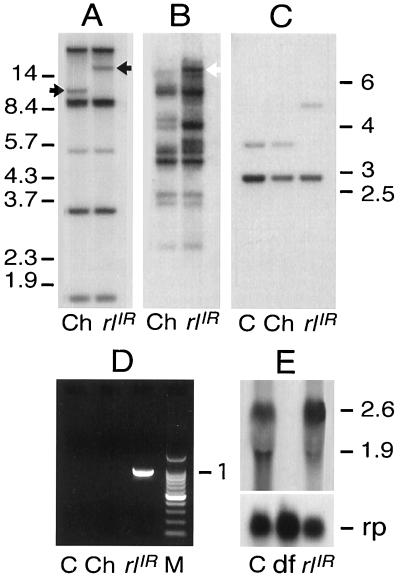
Figure 2.
(A) Southern hybridization of genomic DNA from the Charolles parental strain (Ch) carrying the rl+ allele, and from rlIR1 homozygotes (rlIR), digested with EcoRI and probed with the 1.4-kb rl cDNA probe (30); black arrows indicate the bands whose mobility varies in the rlIR1 mutant and in the Charolles strain. (B) Filters were stripped and reprobed with I sequences; the open arrow indicates I-homologous sequences in the dysgenic mutants that comigrate with rl homologous sequences. (C) Southern hybridization of genomic DNA from Canton-S (C) and Charolles (Ch) parental stains carrying the rl+ allele, and from rlIR1 homozygotes (rlIR), digested with EcoRV and probed with the HindIII–DraI fragment. (D) PCR amplification reaction from genomic DNA of Canton-S (C), Charolles (Ch), and rlIR1 strains. A 982-bp fragment was specifically amplified from genomic DNA of rlIR1 homozygotes. M, molecular weight marker. (E) Northern blot assays of second-instar larvae total RNA from rl+, rlIR1, and Df(2Rh)Rspi1 homozygotes lacking the rl gene. The 1.4-kb rl cDNA probe reveals two major transcripts of 2.6 kb and 1.9 kb, both absent in larvae homozygous for Df(2Rh)Rspi1. The same filter was reprobed with the rp49 ribosomal protein gene probe as a loading control.