Figure 3.
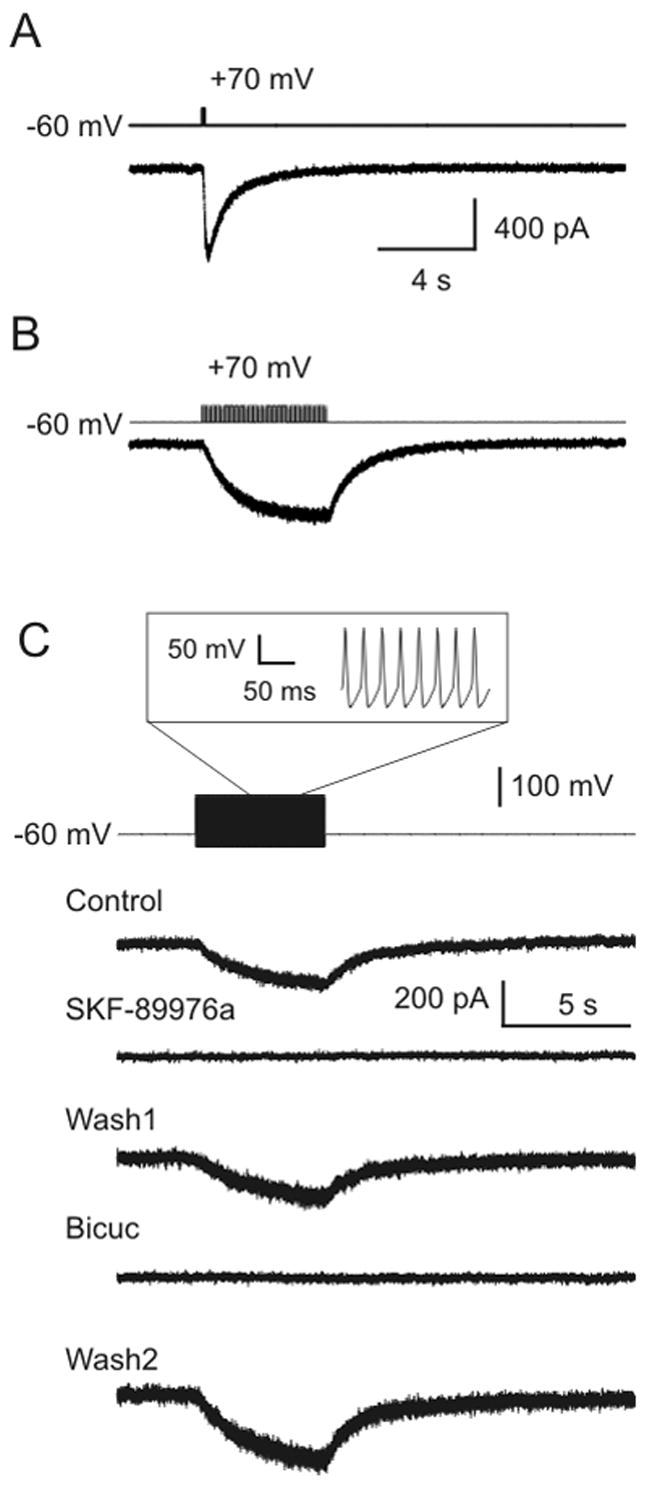
GAT-1 reverses during simulated action potentials. A) A single depolarizing 100 ms square wave pulse from −60 mV to +70 mV induced a large response in a sniffer cell. B) Current was also induced in a sniffer cell by a train of 10 ms depolarizing pulses from −60 mV to +70 mV (frequency 10 Hz; train duration 5 s). C) Simulated action potentials induced a response in a sniffer cell. The command voltage for the GAT-1 cell was a waveform (inset) that simulated a train of action potentials at a rate of 40 Hz. The resting potential was −60 mV, peak voltage was +40 mV, and action potential duration was 6 ms. The response in the sniffer cell was due to GABA release via GAT-1 reversal, because it was blocked by both SKF-89976a (40 μM) and bicuculline (50 μM).
