Fig. 3.
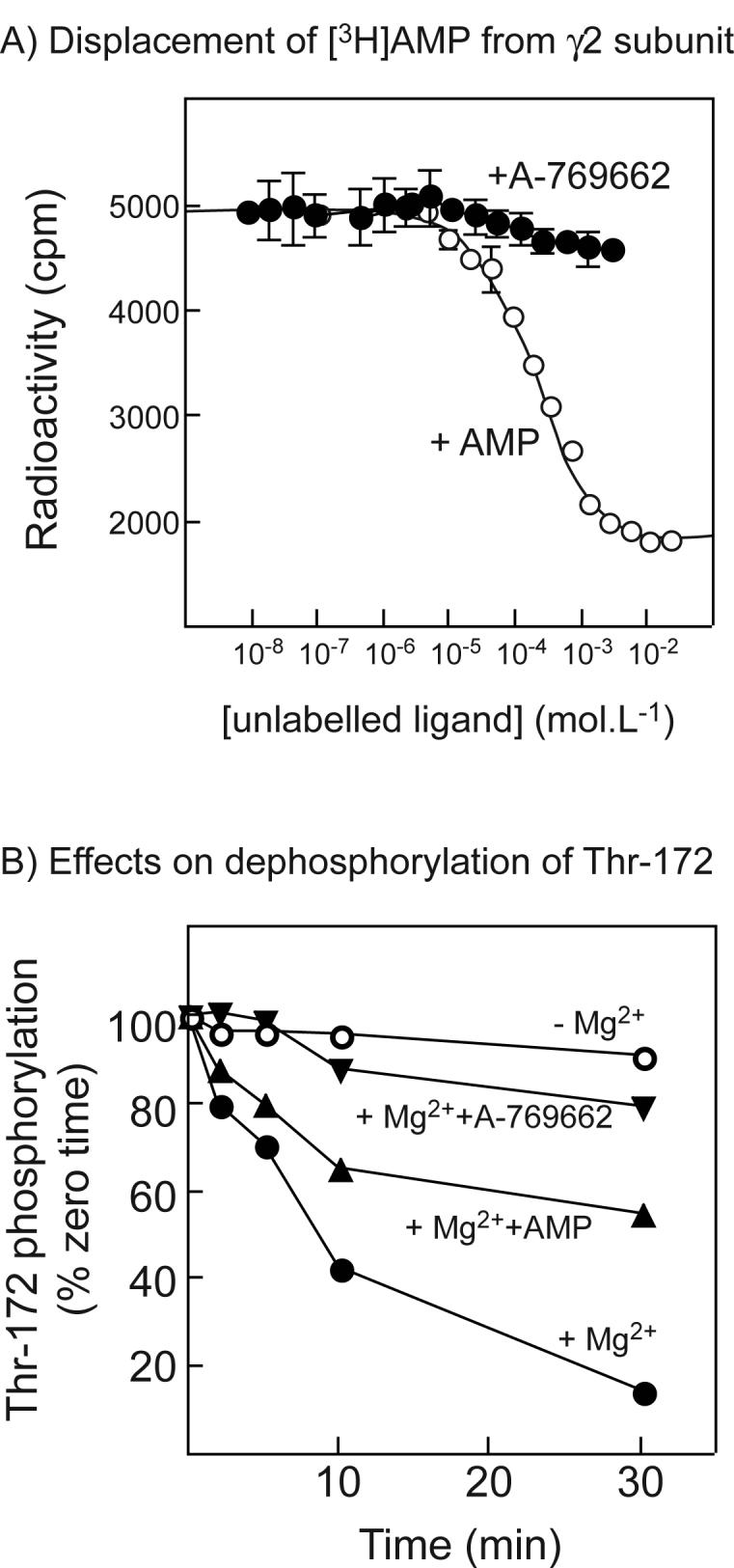
(A) Displacement of [3H]AMP by unlabelled AMP or A-769662 from a GST fusion with the twin Bateman domains of human γ2; (B) Effects of A-769662 on dephosphorylation of AMPK. (A) A GST-γ2 fusion (CBS1-4 (4)) was bound to scintillation proximity beads coated with glutathione, incubated with 120 μM AMP and increasing concentrations of AMP (open circles) or A-769662 (filled circles). Bound radioactivity was determined with a scintillation counter. Data for AMP binding were fitted using GraphPad Prism to the equation Radioactivity = (Maximum.(labelled AMP))/([labelled AMP] + [unlabelled AMP] + KdAMP) + Background. The curve is the theoretical curve generated using the best-fit parameters obtained (Maximum = 5200 cpm; Background = 1800 cpm; KdAMP = 60 ± 15 μM (±SEM)). (B) Purified rat liver AMPK was incubated with protein phosphatase-2Cα (9 ng) without Mg2+ or other addition (open circles), or with 5 mM MgCl2 in the absence (filled circles) or presence of 200 μM AMP (triangles) or 1 μM A-769662 (inverted triangles). Samples were withdrawn at various times and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-pT172 antibody. Intensities of the signal were estimated using the Li-Cor Odyssey infra-red scanner, and results expressed as the percentage of zero time intensity.
