Figure 1.
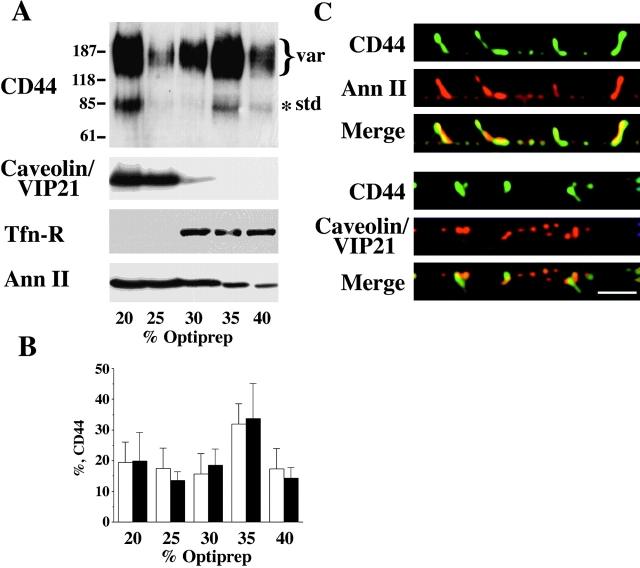
CD44 and annexin II are recovered in the lipid raft fractions and colocalize in the basolateral plasma membrane of EpH4 cells. Cells were lysed in buffer containing 1% Triton X-100 on ice in the absence of Ca2+-chelating agents. Floatation was performed in Optiprep™ gradients and fractions were collected, precipitated, and then equal amounts of total proteins were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies to CD44, caveolin/VIP21, transferrin receptor (Tfn-R), and annexin II (A). Anti-panCD44 antibody IM 7.8.1 recognizes a standard 85-kD isoform and a number of high molecular mass variant isoforms. CD44 and caveolin/VIP21 are localized to the floated raft fractions. As expected, the control protein transferrin receptor could not be floated to the lipid raft fraction. The bulk of a lipid-binding protein annexin II can be found in the lipid raft fraction, too. Molecular mass markers are given in kilodaltons. When fractions from the Optiprep™ gradients were loaded by yield, the total efficiency of CD44 partition into the lipid rafts was determined as a result of three independent experiments (B). The mean percentages of standard (empty bars) and variant (full bars) CD44 isoforms with standard deviations are given. Confluent filter-grown monolayers of EpH4 were fixed in acetone and methanol and subjected to indirect immunofluorescence using anti-CD44 plus anti–annexin II or anti-CD44 plus anti-caveolin/VIP21 antibodies, respectively. Vertical (x-z axis) section images taken by confocal microscopy and image processing (see Materials and Methods) are shown. CD44 colocalized with annexin II in the basolateral plasma membrane (C, upper panel). However, CD44 virtually did not colocalize with caveolin/VIP21 (C, lower panel). Bar, 10 μm.