Figure 7.
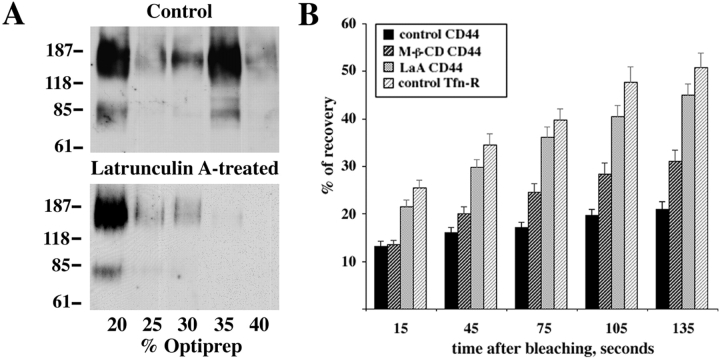
CD44-containing lipid rafts interact with the actin cytoskeleton. To further assess the possibility of the direct interaction of CD44-containing lipid rafts with the actin cytoskeleton, the Optiprep™ gradient floatation following the disruption of the actin cytoskeleton by latrunculin A was performed. A vast majority of CD44 was now found in the floating lipid rafts–rich fraction (A, lower panel) in comparison with control cells (A, upper panel). Molecular mass markers are given in kilodaltons. The measurements of FRAP of CD44 in the plasma membrane of EpH4 cells were made as described in Materials and Methods and percentages of recovery of labeled proteins are shown (B). The lateral mobility of CD44 was dependent on the intact actin cytoskeleton and the presence of the plasma membrane cholesterol. The transmembrane protein of clathrin-coated pits, the transferrin receptor, was used as a control. Mean ± SE values are shown.