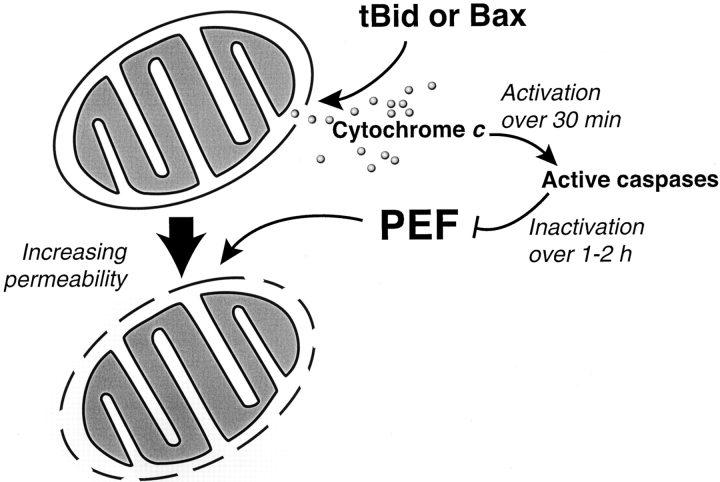
Figure 10.
Model of two types of mitochondrial outer membrane permeability observed in Xenopus extracts during apoptosis. Mitochondria treated with tBid or Bax in buffer undergo efflux of endogenous cytochrome c (12 pmol/μl mitochondria) across the outer membrane, with limited permeability to exogenous cytochrome c. Additional exposure to cytosol (PEF) allows high permeability to exogenous cytochrome c (60 nmol/μl mitochondria per min, as measured by the rate of the complex IV reaction). Thus, this increased exchange of endogenous cytochrome c is at least ∼5,000 times the rate of cytochrome c efflux after tBid or Bax treatment, assuming that all of the mitochondrial cytochrome c is released over 1 min. PEF begins to act immediately after tBid–induced permeabilization, but is inactivated over 1–2 h by caspase activation. The inner membrane appears unaffected.