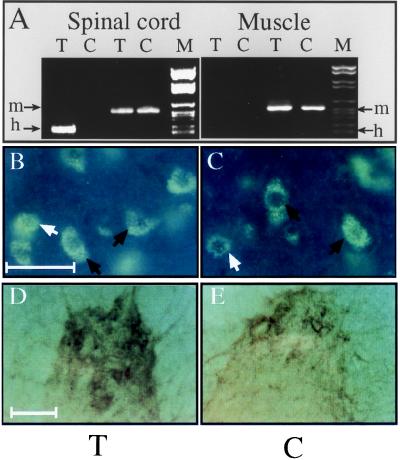
Figure 1.
Human AChE cDNA is expressed in spinal cord neurons but not muscle. (A) RT-PCR analyses. Primers specific for mouse (m) or human (h) AChE mRNA indicates expression of the transgene in transgenic (T) spinal cord, but not muscle. Control (C) mice express the endogenous mRNA in both tissues. (B and C) In situ hybridization. A probe detecting both mouse and human AChE mRNAs labeled neurons in 50-μm cervical spinal cord sections from both transgenic (B) and control (C) mice. Black arrows indicate large polygonal α motoneurons; white arrows indicate γ motoneurons and/or interneurons. ELF kit 6605 (Molecular Probes) diluted 1:250 was used for detection. (Size bar, 50 μm.) Note that labeling is restricted to cells with neuronal morphology. (D and E) Enzyme activity. Fixed sections from the anterior horn of lumbar spinal cord of transgenic (D) or control (E) mice were cytochemically stained for catalytically active AChE. Note the enhanced activity in nerve fibers and cell bodies from the transgenic spinal cord. (Size bar, 100 μm.)