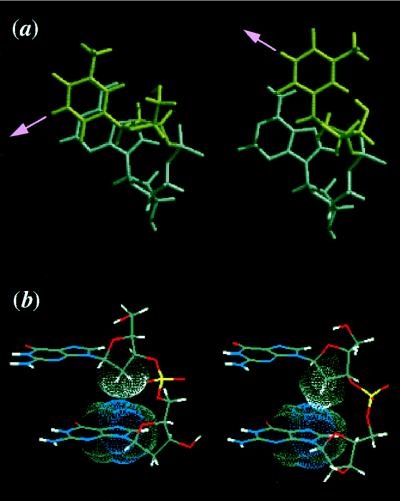
Figure 3.
Base rotation by interconversion of sugar puckers. (a) Top view of the base rotation caused by interconversion of the sugar puckers. The sugar pucker of the 5′-residue (T, top) is in the S-type (Left) and the N-type (Right), whereas that of the 3′-residue (A, bottom) is fixed in the S-type. Note that the hydrogen-bonding vector is rotated toward its major groove by the conversion from the S-type to the N-type. (b) Two types of deoxyribose-base stacking. All residues are in the S-type sugar pucker (Left) or the N-type (Right) sugar pucker.