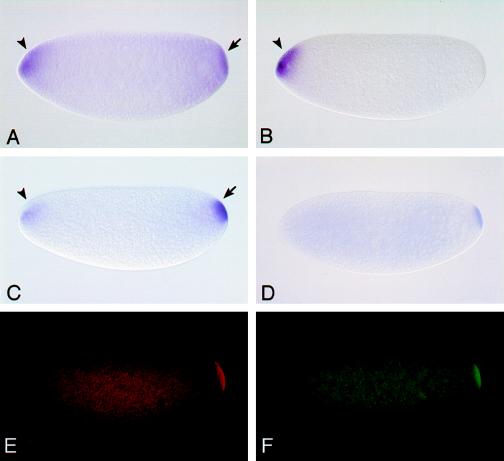
Figure 1.
Effect of ribozymes on the distribution of mtlrRNA and polar plasm components in the late-cleavage embryos at around 60 min after egg laying. In situ hybridization of the mtlrRNA cDNA probe to a control embryo injected with DW (A) and an embryo injected with RbzJ and RbzK (B). Note that mtlrRNA signal in polar plasm completely disappears in a ribozyme-injected embryo (B). Arrow in A shows mtlrRNA signal. As an internal control for in situ hybridization, the embryos also were hybridized with a probe detecting bcd mRNA that localizes at the anterior pole region of early cleavage embryos (39, 40). Arrowheads in A-C indicate bcd mRNA signal. In situ hybridization of osk cDNA probe (C) and gcl cDNA probe (D) to the ribozyme-injected embryos. Arrow in C shows osk mRNA signal. Immunostaining of VAS (E) and TUD (F) in the ribozyme-injected embryos. osk mRNA, gcl mRNA, VAS, and TUD normally accumulated in polar plasm of the ribozyme-injected embryos. Lateral views of the late cleavage embryos are shown; anterior is to left.