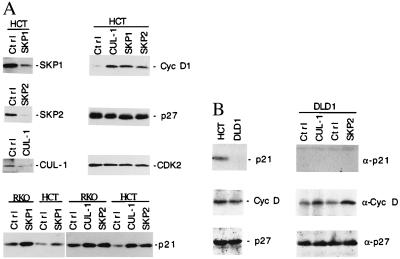
Figure 4.
Selective stabilization of the cellular cyclin D and p21 proteins by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides against SKP1, SKP2, or CUL-1. (A, Upper Left) HCT116 (HCT) cells were transfected with antisense oligonucleotides against SKP1, SKP2, CUL-1, or a control oligonucleotide (Ctrl) by using cytofectin GS2888 as indicated on top of each lane. Eighteen hours after transfection, each protein was immunoprecipitated and quantitated by immunoblotting analysis using the specific antibody as indicated on the right, respectively. (A, Upper Right and Lower) HCT116 or RKO cells were treated with control or antisense oligonucleotides against CUL-1, SKP2, or SKP1 RNA as indicated on the top of each panel. The relative protein levels of cyclin D, p27, CDK2, and p21 from the treated HCT116 or RKO cells (0.5 × 106 each) were compared by immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting analyses using their respective antibodies. (B, Left) The relative levels of p21, cyclin D, and p27 from HCT116 (p53 positive) and DLD1 (p53 negative) cells (0.5 × 106 each) were compared by using immunoprecipitation and Western blotting analyses. (B, Right) DLD1 cells were transfected with antisense oligonucleotides against SKP1, SKP2, CUL-1, or a control oligonucleotide (Ctrl) as indicated on the top of the lanes. The antisense effects on the protein levels of p21, cyclin D, and p27 were examined by the Western blot analysis as described in A.