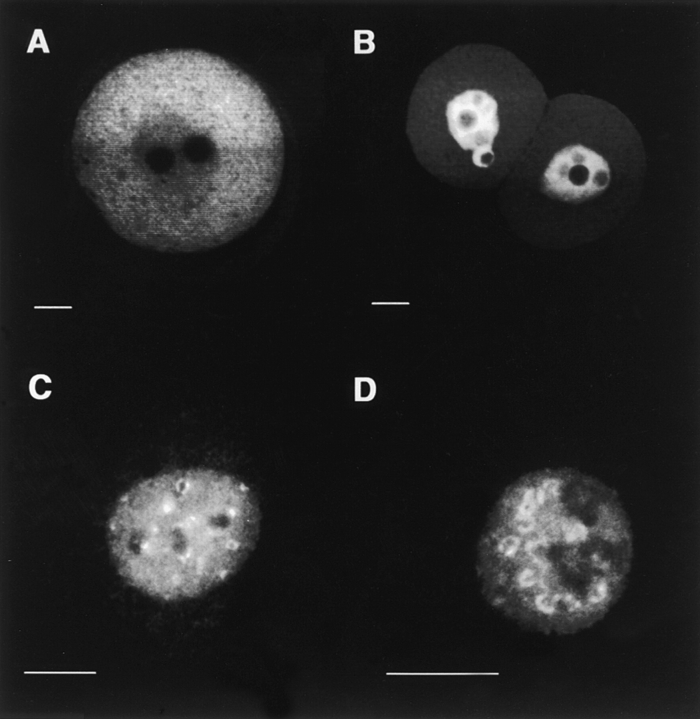
Figure 5.
Cytoplasmic retention of Dnmt1 is independent of protein size. Two β-galactosidase fusion constructs were generated, one containing amino acids 1–854 of Dnmt1 (depicted in the diagram, Fig. 4 I) and the other containing amino acids 1–796 of human DNA ligase I (Cardoso et al. 1997). The size of both fusion proteins is between 160–170 kD. Both plasmids were transfected into mouse fibroblasts and microinjected into fertilized mouse eggs. After a 1-d incubation, localization of the fusion proteins was assayed by immunofluorescence staining with anti–β-galactosidase monoclonal antibody. A shows a confocal section through the middle of a mouse embryo expressing the Dnmt1 fusion which is mostly cytoplasmic. B shows the DNA ligase I fusion expressed in mouse embryos, which clearly has an exclusive nuclear localization. C and D illustrate the localization of the same proteins as in A and B, respectively, in the nuclei of tissue culture cells, in these images undergoing S-phase as seen by the ring and dot-shaped pattern of subnuclear foci (Leonhardt et al. 1992; Cardoso et al. 1997). Bar 10 μm.