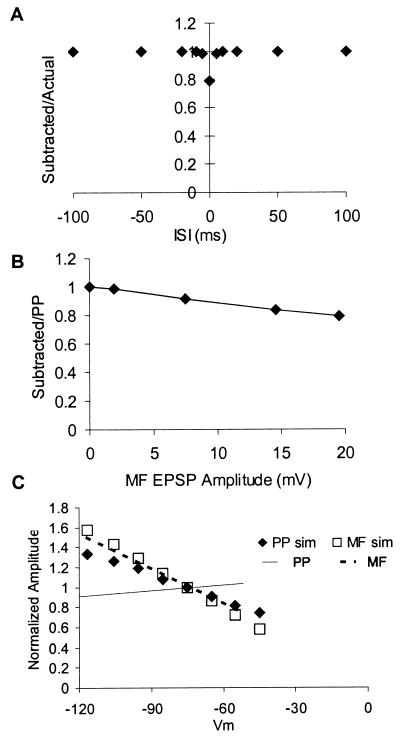
Figure 4.
Simulations show that passive model cannot account for observed nonlinearities. Unless otherwise stated, data from simulations were analyzed in the same manner as data from the experiments. (A) Compare with Fig. 2D. Simulations show the effect of mossy fiber EPSP amplitude on the linearity of EPSP summation. Passive sublinearity increases almost linearly with mossy fiber EPSP amplitude, with a 20-mV EPSP resulting in the subtracted response being 80% of the unpaired response. (B) Compare with Fig. 1C. The dependence of summation on ISI for this same simulated 20-mV EPSP shows that the passive sublinearity is restricted to very short ISIs. (C) Compare with Fig. 3A. (B) Comparison of simulated and actual data on the effect of somatic depolarization on perforant path and mossy fiber EPSPs. The voltage dependence of perforant path EPSPs (——) line, expressed as the average best fit line through data from like those shown in Fig. 3A taken from N = 12 cells) is inconsistent with the voltage dependence predicted for synapses on the distal-most dendrites of a CA3 cell (♦). The voltage dependence of real (–––, N-6) and simulated (□) mossy fiber EPSPs are almost identical.