Abstract
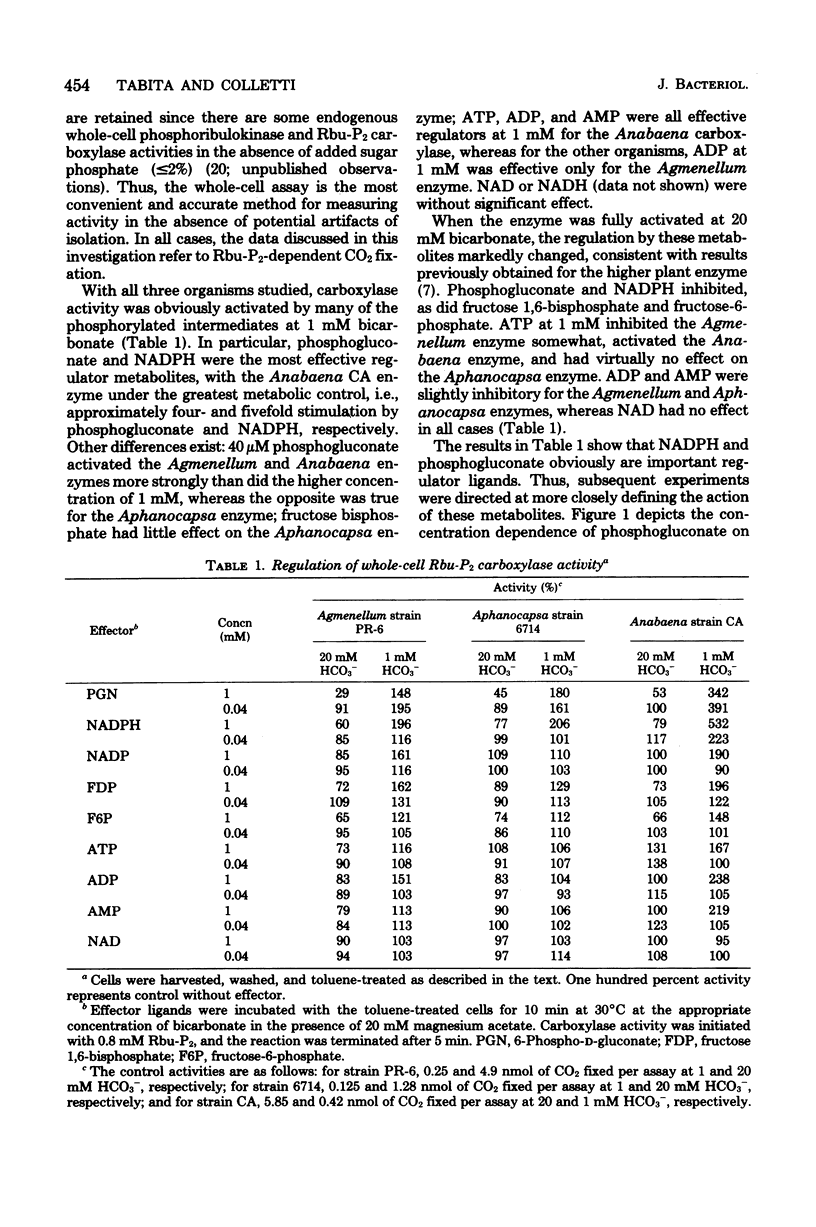
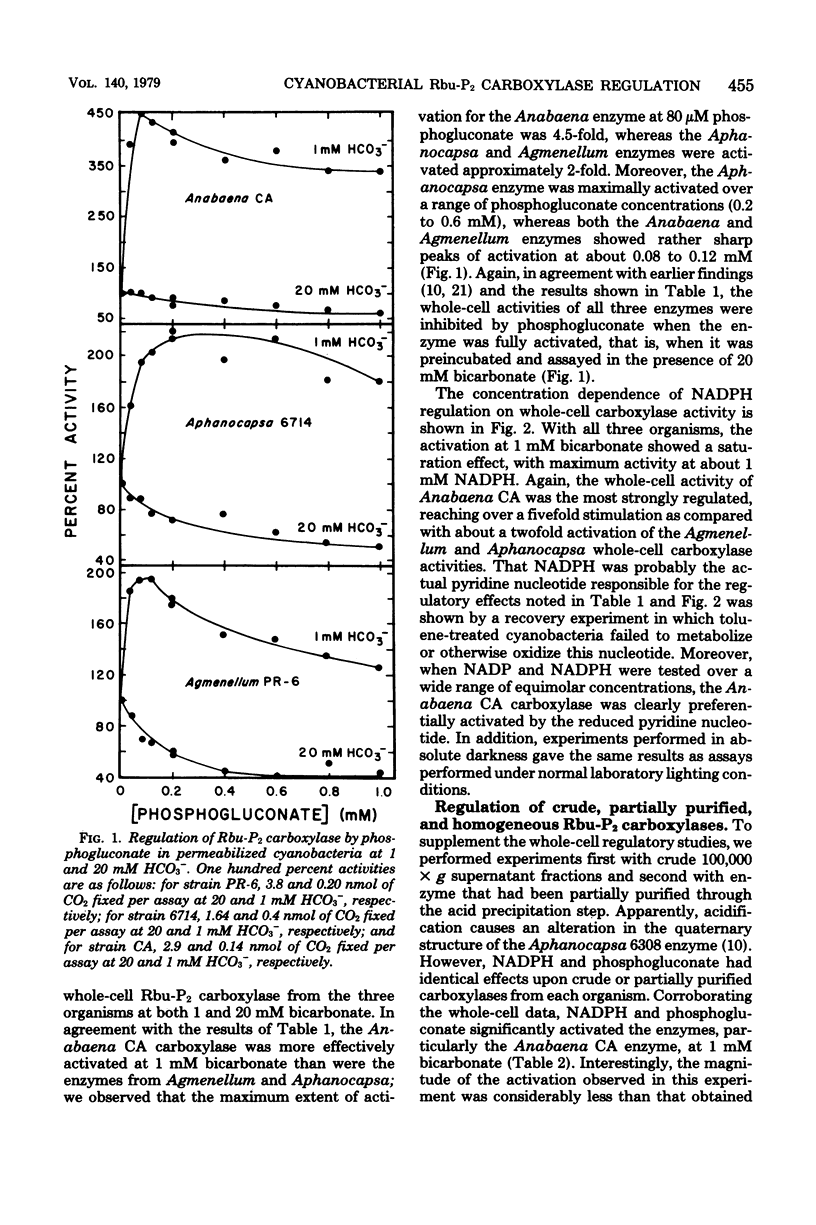
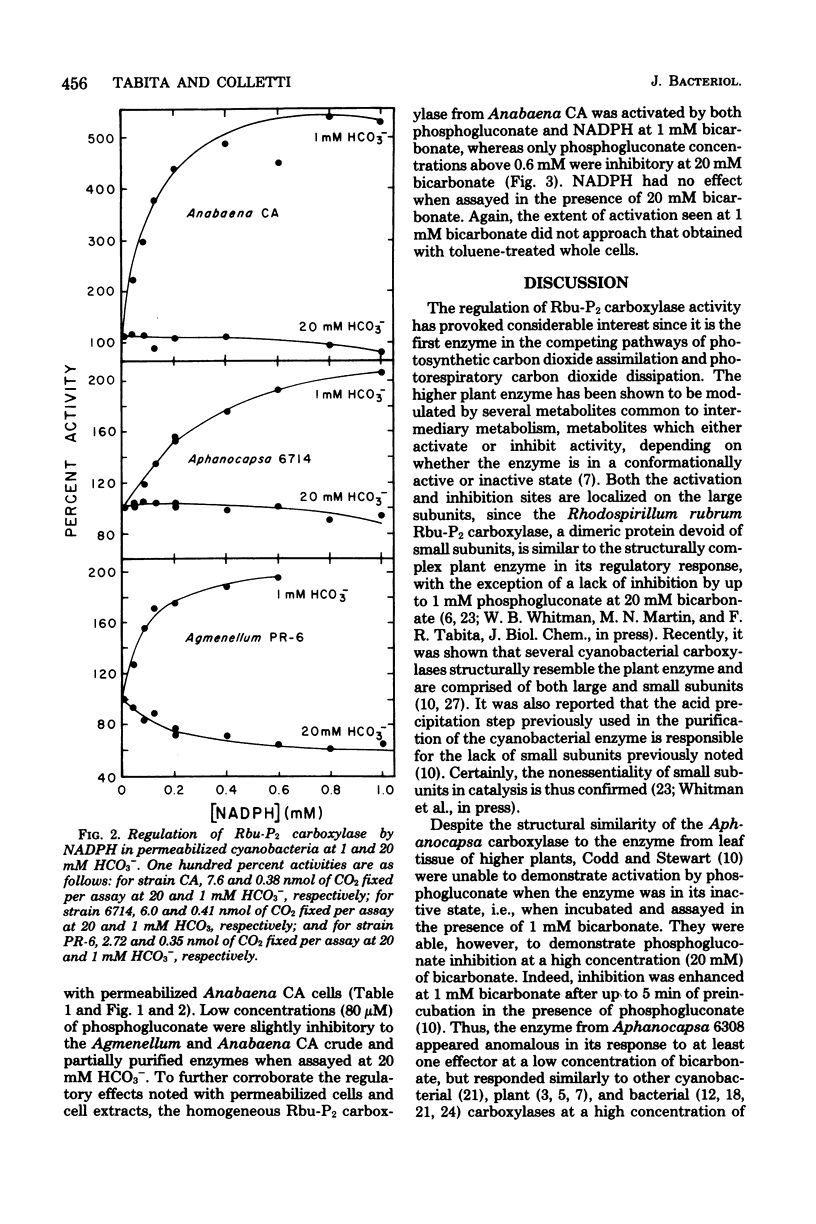
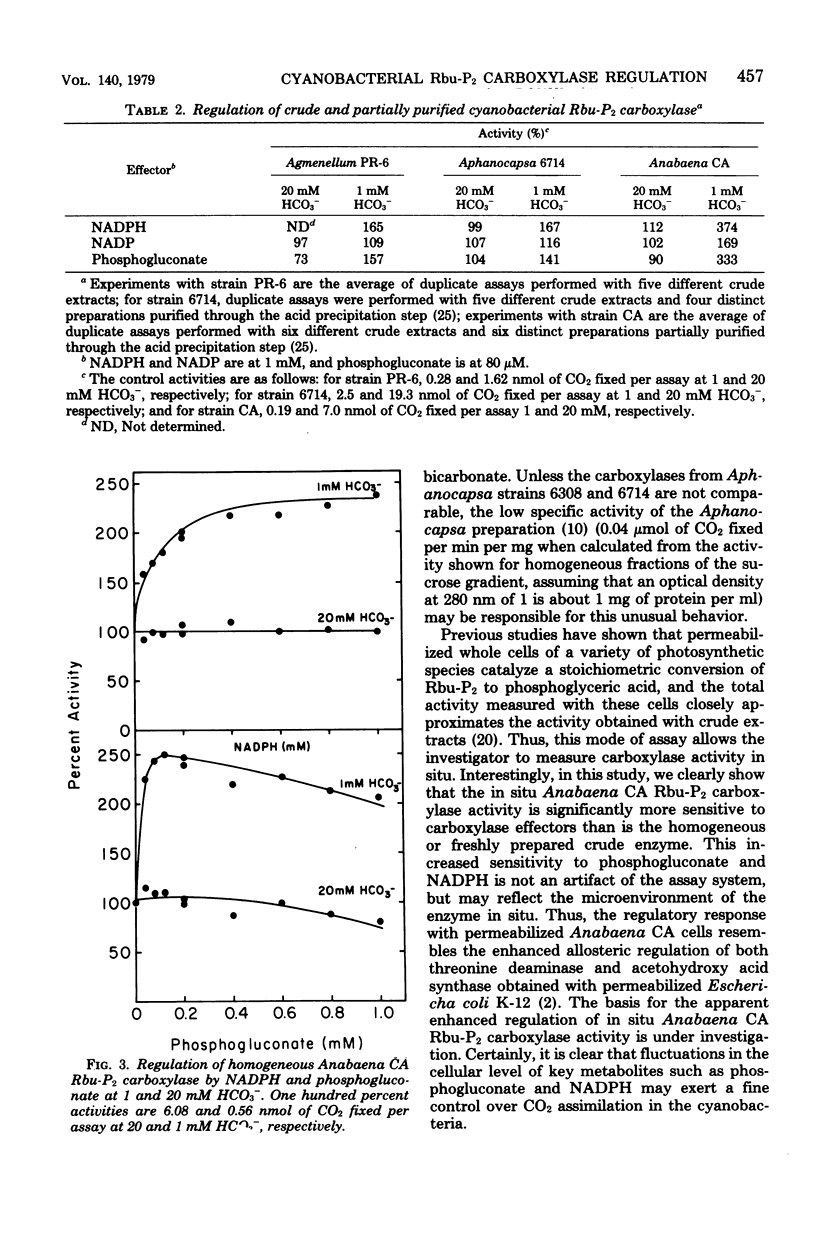
Cyanobacteria assimilate carbon dioxide through the Calvin cycle and therefore must regulate the activity of ribulose 1,5-bisophosphate carboxylase. Using an in situ assay, as well as measuring the activity in crude, partially purified, and homogeneous preparations, we can show that a number of phosphorylated intermediates exert a regulatory role. Three diverse organisms, Agmenellum quadruplicatum, Aphanocapsa 6714, and Anabaena sp. CA, were studied, and it was found that the in situ and cell-free carboxylase activities were particularly affected by low levels of phosphogluconate and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. There was a marked activation by these ligands when the inactive enzyme was assayed in the presence of low levels of bicarbonate, a result significantly different from a previous report. Moreover, the fully activated enzyme was inhibited by phosphogluconate. In situ Anabaena CA carboxylase activity exhibited a particular capacity for activation by phosphogluconate and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. However, activation of the crude, partially purified, or homogeneous Anabaena CA carboxylase by phosphogluconate and reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate was significantly decreased when compared with enzyme activity in permeabilized cells. It appears that the microenvironment or the conformation of the enzyme within the cell may be significantly different from that of the isolated enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blatt J. M., Jackson J. H. Enhanced allosteric regulation of threonine deaminase and acetohydroxy acid synthase from Escherichia coli in a permeabilized-cell assay system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 11;526(1):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90311-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes G., Ogren W. L. Oxygen inhibition and other properties of soybean ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Apr 10;247(7):2171–2176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchanan B. B., Schürmann P. Regulation of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase in the photosynthetic assimilation of carbon dioxide. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):4956–4964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chollet R., Anderson L. L. Regulation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase activities by temperature pretreatment and chloroplast metabolites. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Sep;176(1):344–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90173-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christeller J. T., Laing W. A. A kinetic study of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochem J. 1978 Aug 1;173(2):467–473. doi: 10.1042/bj1730467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Activation and inhibition of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phosphogluconate. Plant Physiol. 1973 Oct;52(4):373–379. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.4.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Activation of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate and other chloroplast metabolites. Plant Physiol. 1974 Oct;54(4):556–559. doi: 10.1104/pp.54.4.556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu D. K., Bassham J. A. Regulation of ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by substrates and other metabolites: further evidence for several types of binding sites. Plant Physiol. 1975 Apr;55(4):720–726. doi: 10.1104/pp.55.4.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson J. L., Tabita F. R. Different molecular forms of D-ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):943–949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. W., DeMoss J. A. Effects of toluene on Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1420–1425. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1420-1425.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawlis V. B., Gordon G. L., McFadden B. A. Regulation of activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase from Pseudomonas oxalaticus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Oct 16;84(3):699–705. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90761-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelroy R. A., Bassham J. A. Photosynthetic and dark carbon metabolism in unicellular blue-green algae. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;86(1):25–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00412397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelroy R. A., Levine G. A., Bassham J. A. Kinetics of light-dark CO2 fixation and glucose assimilation by Aphanocapsa 6714. J Bacteriol. 1976 Nov;128(2):633–643. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.2.633-643.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purohit K., McFadden B. A. Ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and oxygenase from Thiocapsa roseopersicina: activation and catalysis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Apr 15;194(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90599-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., Caruso P., Whitman W. Facile assay of enzymes unique to the Calvin cycle in intact cells, with special reference to ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Anal Biochem. 1978 Feb;84(2):462–472. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. D-ribulose 1,5-diphosphate carboxylase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. I. Levels, purification, and effects of metallic ions. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3453–3458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. Molecular and catalytic properties of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from the photosynthetic extreme halophile Ectothiorhodospira halophila. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jun;126(3):1271–1277. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.3.1271-1277.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. One-step isolation of microbial ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(3):231–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00696237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., McFadden B. A. Regulation of ribulose-1,5-diphosphate carboxylase by 6-phospho-D-gluconate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Sep 5;48(5):1153–1159. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90831-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., Stevens S. E., Jr, Gibson J. L. Carbon dioxide assimilation in blue-green algae: initial studies on the structure of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.531-539.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita R. F., Stevens S. E., Jr, Quijano R. D-ribulose 1, 5-diphosphate carboxylase from blue-green algae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Nov 6;61(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Nishimura M., Akazawa T. Presence of two subunit types in ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase from blue-green algae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91179-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman W., Tabita F. R. Inhibition of D-ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase by pyridoxal 5'-phosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 23;71(4):1034–1039. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90758-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Smet M. J., Kingma J., Witholt B. The effect of toluene on the structure and permeability of the outer and cytoplasmic membranes of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Jan 4;506(1):64–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90435-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


