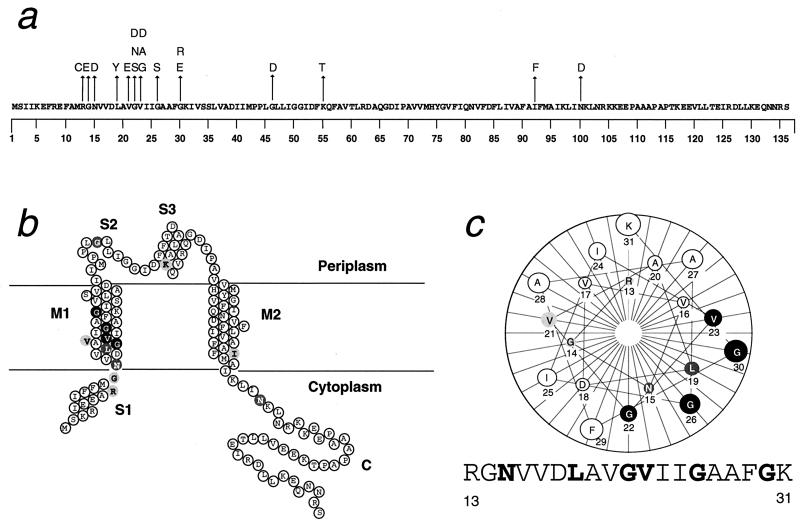
Figure 3.
(a) Amino acid substitutions in gain-of-function mutants displayed on the wild-type MscL sequence. (b) Locations of mutated sites diagrammed on a membrane topology model of a MscL subunit. (c) A helical wheel of the inner half of M1, showing the clustering to one side the sites at which mutations have severe effects. In b and c, the dark gray and light gray symbols signify sites that can be mutated to give very severe (Group 1 in Table 1), only the less severe (Group 2 and 3), or only very mild (Group 4) mutants, respectively. The mutations are R13C (3;1+1*, i.e., three independent isolates from hydroxylamine mutageneses; and two from error-prone PCRs, one of which, marked with ∗, is a multiple mutant with one or more additional substitutions outside residue 13 through 30), G14E (1;0), N15D (0;3+1*), L19Y (1;2*), V21E (0, 1+2*), G22S (1;0), G22N (1;0), G22D (1*, 2), V23G (0, 1), V23A (0, 4+2*) V23D (0, 1+3*), G26S (2+3*;3+2*), G30E (5;1), G30R (3;0), G46D (3, 1), K55T (0;1), I92F (0;1), and N100D (0;1).