Abstract
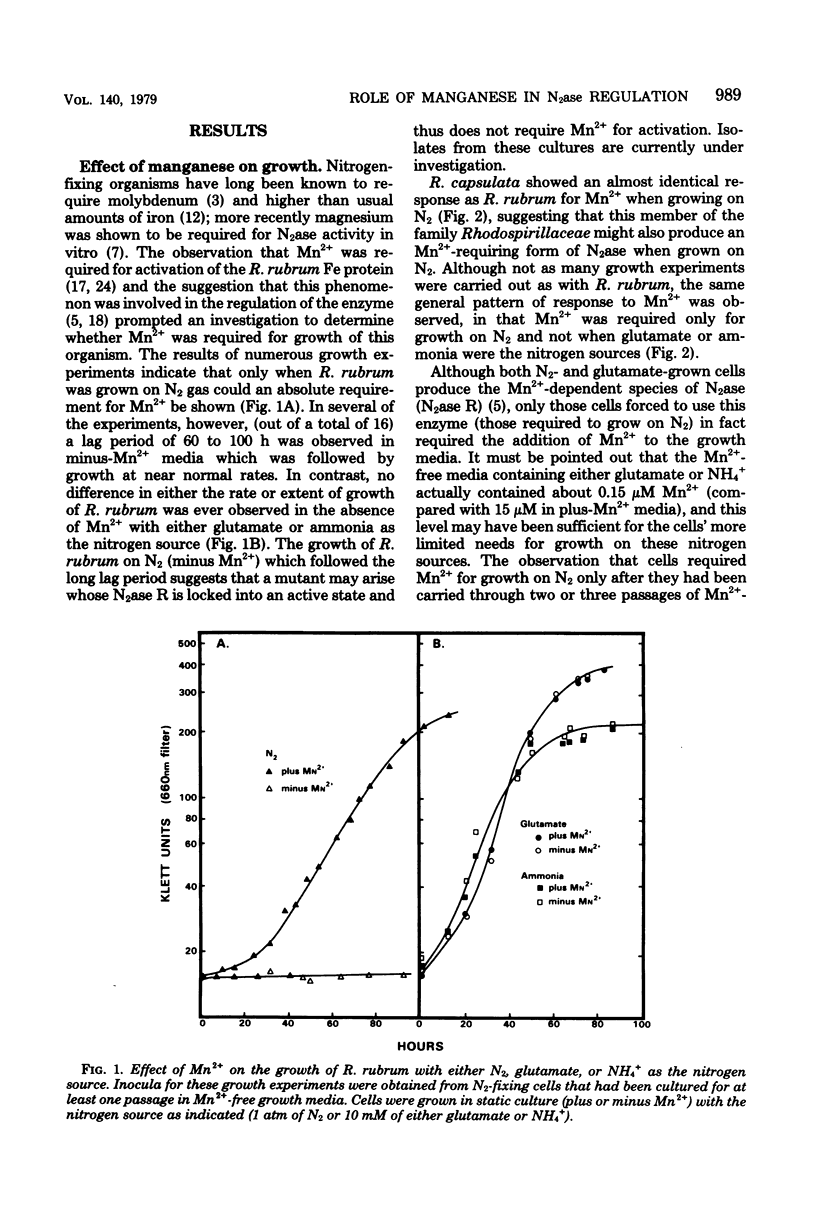
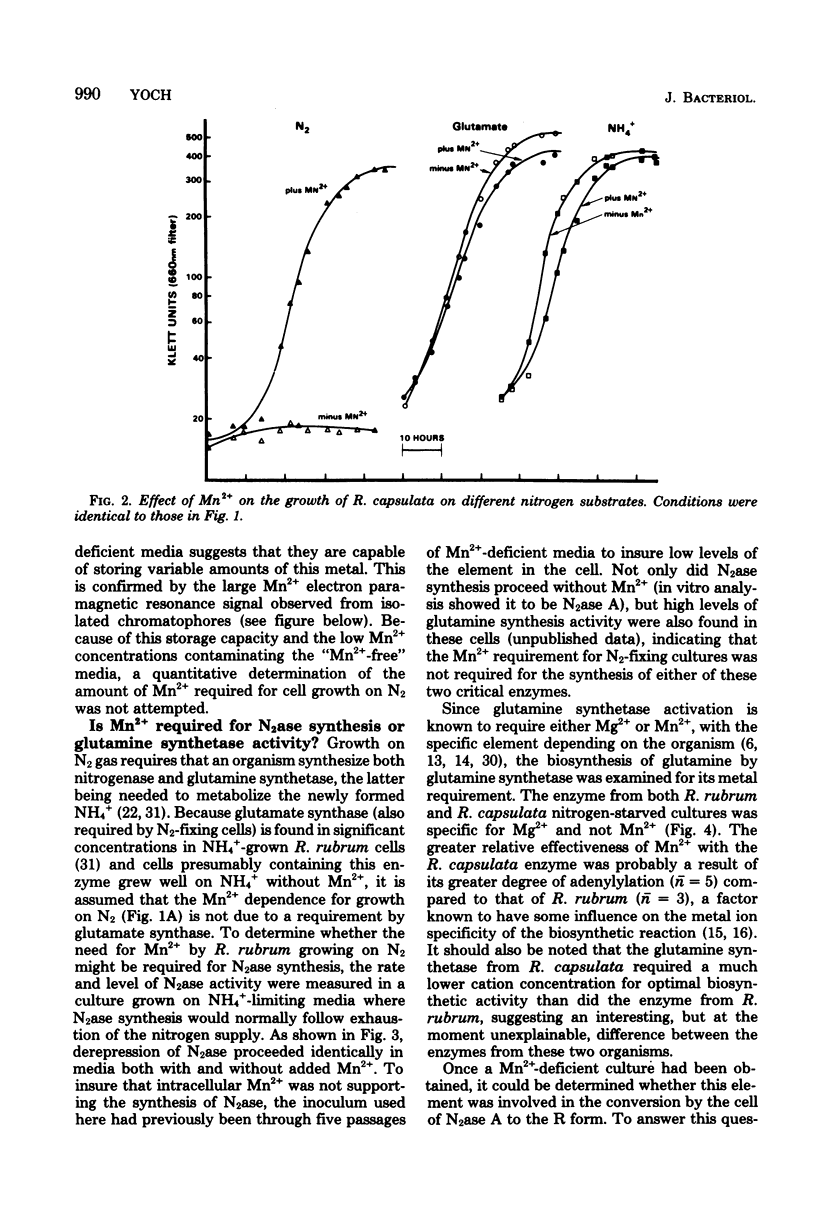
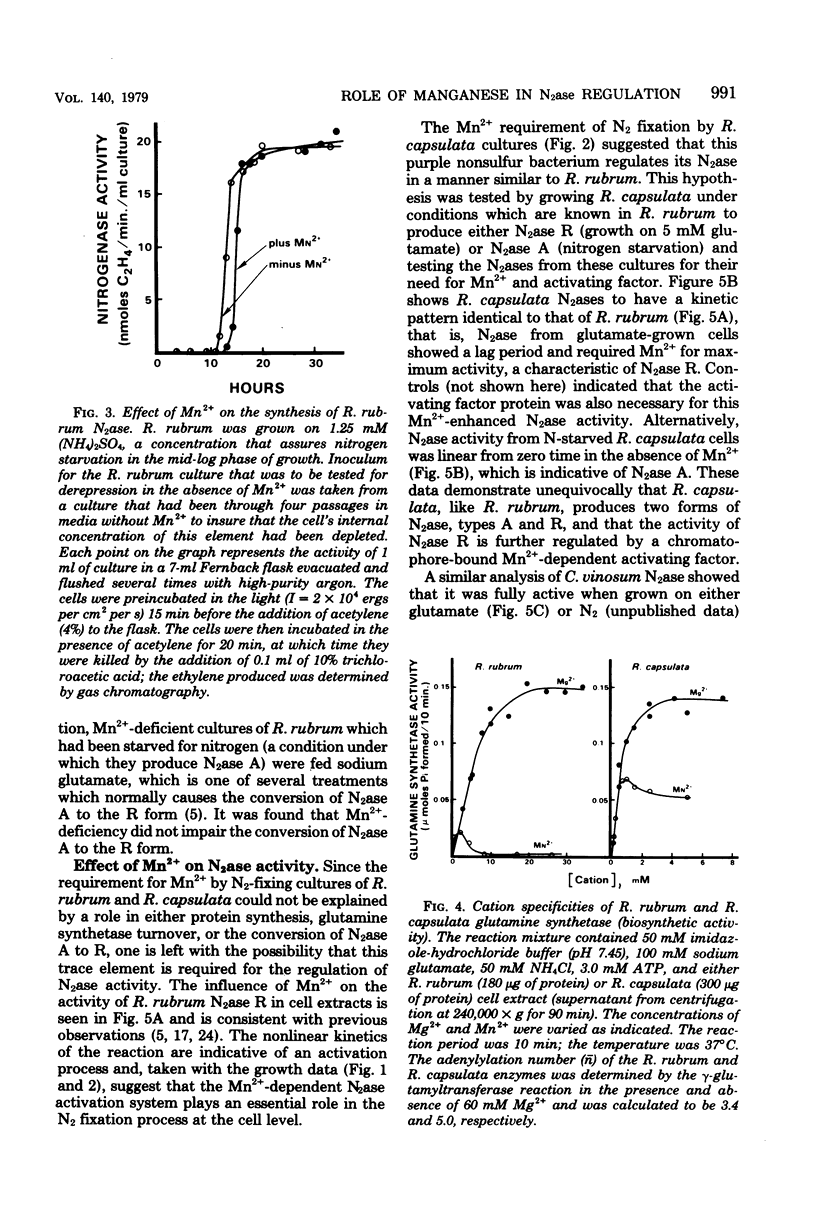
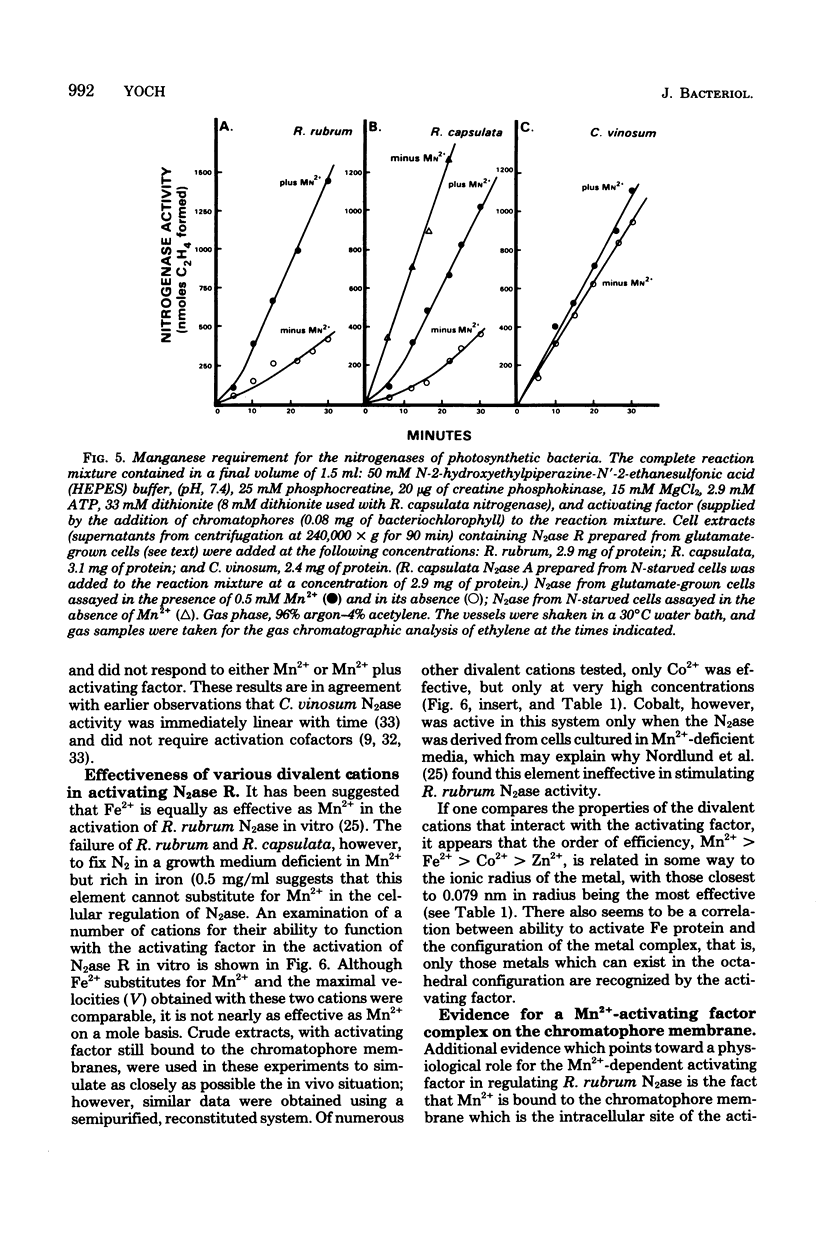
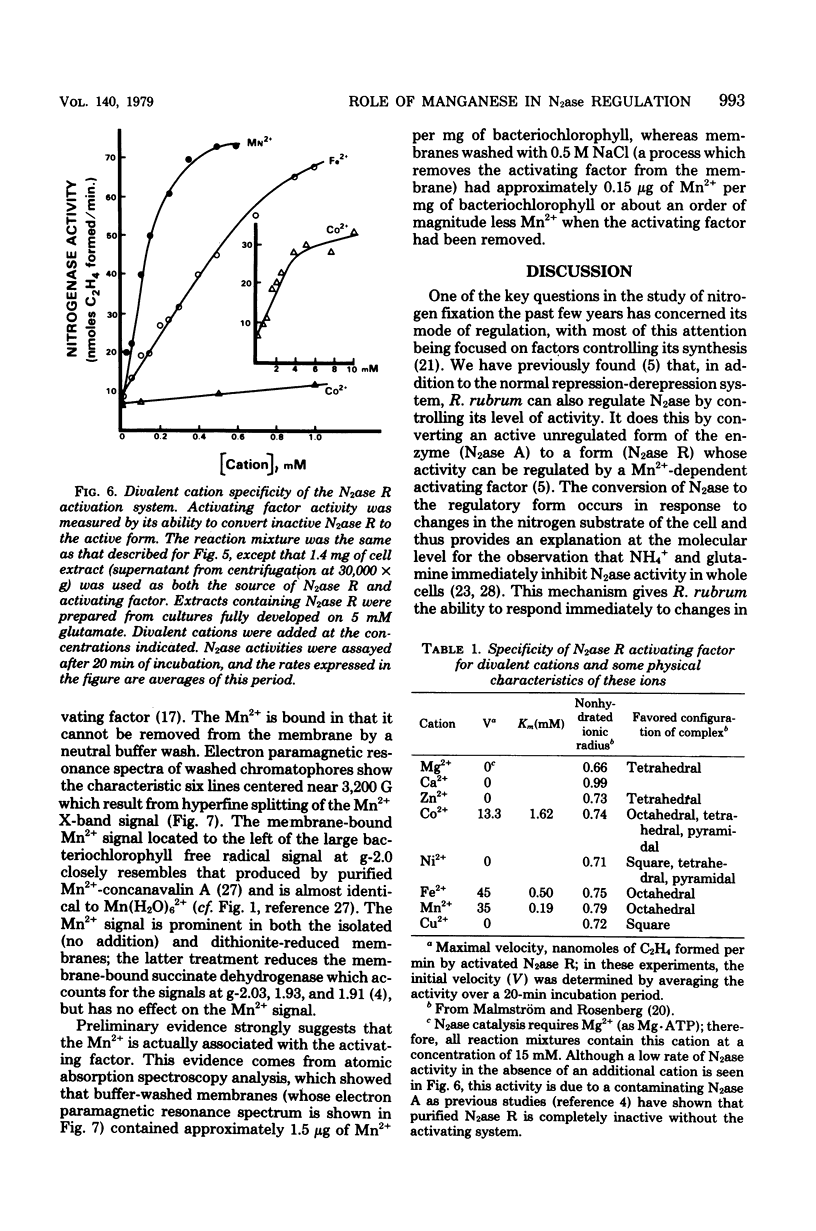
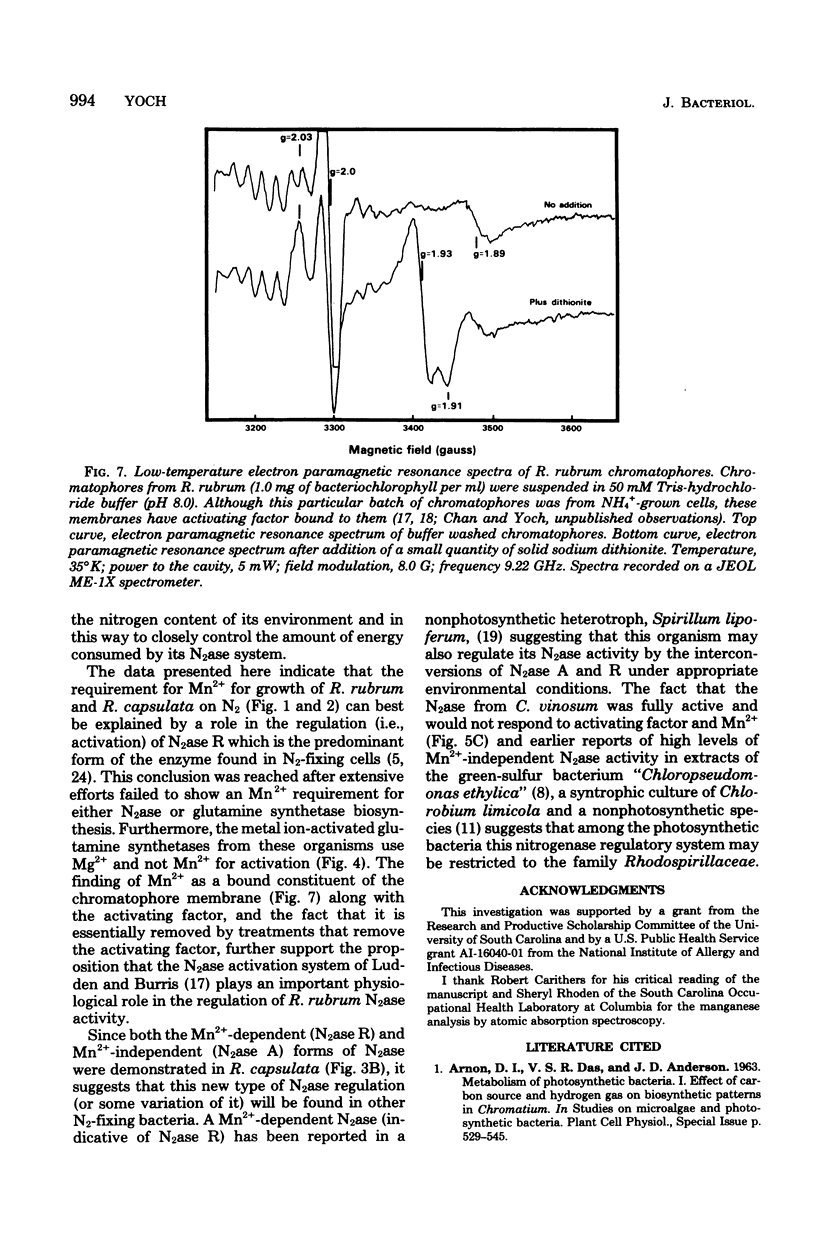
Nitrogenase (N2ase) from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum can exist in two forms, an unregulated form (N2ase A) and a regulatory form (N2ase R), the latter being identified in vitro by its need for activation by a Mn2+-dependent N2ase activating system. The physiological significance of this Mn2+-dependent N2ase activating system was suggested here by observations that growth of R. rubrum and Rhodopseudomonas capsulata on N2 gas (a condition that produces active N2ase R) required Mn2+, but growth on ammonia or glutamate did not. Manganese could not be shown to be required for the biosynthesis of either nitrogenase or glutamine synthetase or for glutamine synthetase turnover, but it was required for the in vitro activation of N2ases from N2 and glutamate-grown R. rubrum and R. capsulata cells. Chromatium N2ase, in contrast, was always fully active and did not require Mn2+ activation, suggesting that only the purple nonsulfur bacteria are capable of controlling their N2ase activity by this new type of regulatory system. Although R. rubrum could not substitute Fe2+ for Mn2+ in the in vivo N2 fixation process, Fe2+ and, to a lesser extent, Co2+ could substitute for Mn2+ in the in vitro activation of N2ase. Electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy of buffer-washed R. rubrum chromatophores showed lines characteristic of Mn2+. Removal of the Mn2+-dependent N2ase activating factor by a salt wash of the chromatophores removed 90% of the Mn2+, which suggested a specific coupling of this metal to the activating factor. The data presented here all indicate that Mn2+ plays an important physiological role in regulating the N2 fixation process by these photosynthetic bacteria.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender R. A., Janssen K. A., Resnick A. D., Blumenberg M., Foor F., Magasanik B. Biochemical parameters of glutamine synthetase from Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):1001–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.1001-1009.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carithers R. P., Yoch D. C., Arnon D. I. Isolation and characterization of bound ion-sulfur proteins from bacterial photosynthetic membranes. II. Succinate dehydrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum chromatophores. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7461–7467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carithers R. P., Yoch D. C., Arnon D. I. Two forms of nitrogenase from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodospirillum rubrum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dharmawardene M. W., Haystead A., Stewart W. D. Glutamine synthetase of the nitrogen-fixing alga Anabaena cylindrica. Arch Mikrobiol. 1973 Apr 26;90(4):281–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00408924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dilworth M. J., Subramanian D., Munson T. O., Burris R. H. The adenosine triphosphate requirement for nitrogen fixation in cell-free extracts of Clostridium pasteurianum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Jun 22;99(3):486–503. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(65)80202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. C., Telfer A., Smith R. V. The purification and some properties of the molybdenum-iron protein of Chromatium nitrogenase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 15;310(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(73)90114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard J. S., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. V. Partial purification and properties of glutamine synthetase from Bacillus licheniformis. J Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(4):1007–1015. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.4.1007-1015.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. C., Gest H. Adenylylation/deadenylylation control of the glutamine synthetase of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Dec 1;81(2):365–371. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11960.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. C., Gest H. Inorganic nitrogen assimilation by the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Bacteriol. 1976 Nov;128(2):683–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.2.683-688.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingdon H. S., Shapiro B. M., Stadtman E. R. Regulation of glutamine synthetase. 8. ATP: glutamine synthetase adenylyltransferase, an enzyme that catalyzes alterations in the regulatory properties of glutamine synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1703–1710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden P. W., Burris R. H. Activating factor for the iron protein of nitrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Science. 1976 Oct 22;194(4263):424–426. doi: 10.1126/science.824729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden P. W., Burris R. H. Purification and properties of nitrogenase from Rhodospirillum rubrum, and evidence for phosphate, ribose and an adenine-like unit covalently bound to the iron protein. Biochem J. 1978 Oct 1;175(1):251–259. doi: 10.1042/bj1750251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludden P. W., Okon Y., Burris R. H. The nitrogenase system of Spirillum lipoferum. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 1;173(3):1001–1003. doi: 10.1042/bj1731001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortenson L. E. Regulation of nitrogen fixation. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1978;13:179–232. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152813-3.50010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagatani H., Shimizu M., Valentine R. C. The mechanism of ammonia assimilation in nitrogen fixing Bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;79(2):164–175. doi: 10.1007/BF00424923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilson A. H., Nordlund S. Regulation of nitrogenase synthesis in intact cells of Rhodospirillum rubrum: inactivation of nitrogen fixation by ammonia, L-glutamine and L-asparagine. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Nov;91(1):53–62. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-1-53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund S., Eriksson U., Baltscheffsky H. Necessity of a membrane component for nitrogenase activity in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Oct 12;462(1):187–195. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90201-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund S., Eriksson U., Baltscheffsky H. Properties of the nitrogenase system from a photosynthetic bacterium, Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 9;504(2):248–254. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90173-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORMEROD J. G., ORMEROD K. S., GEST H. Light-dependent utilization of organic compounds and photoproduction of molecular hydrogen by photosynthetic bacteria; relationships with nitrogen metabolism. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Sep;94:449–463. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed G. H., Cohn M. Electron paramagnetic resonance spectra of manganese (II)-protein complexes. Manganese (II)-concanavalin A. J Biol Chem. 1970 Feb 10;245(3):662–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schick H. J. Substrate and light dependent fixation of molecular nitrogen in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Mikrobiol. 1971;75(2):89–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00407997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman E. R., Ginsburg A., Ciardi J. E., Yeh J., Hennig S. B., Shapiro B. M. Multiple molecular forms of glutamine synthetase produced by enzyme catalyzed adenylation and deadenylylation reactions. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1970;8:99–118. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(70)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weare N. M., Shanmugam K. T. Photoproduction of ammonium ion from N2 in Rhodospirillum rubrum. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Nov 2;110(23):207–213. doi: 10.1007/BF00690229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter H. C., Arnon D. I. The nitrogen fixation system of photosynthetic bacteria. I. Preparation and properties of a cell-free extract from Chromatium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 3;197(2):170–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Arnon D. I. The nitrogen fixation system of photosynthetic bacteria. II. Chromatium nitrogenase activity linked to photochemically generated assimilatory power. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 3;197(2):180–184. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


