Figure 5.
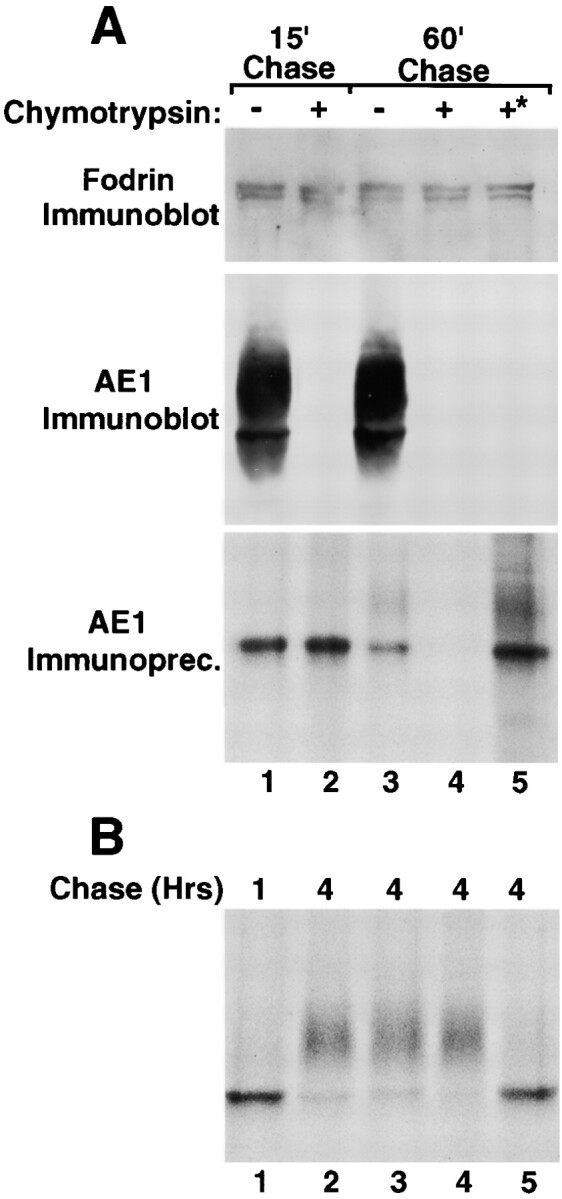
Surface delivery and recycling of newly synthesized AE1-4 anion exchangers. MDCK cells stably expressing AE1-4 were pulsed with 35S-Translabel™ for 15 min, followed by 15 min of chase (A, lane 1). After 15 min of chase, the cells were chased an additional 45 min in the absence (A, lane 3) or presence (A, lane 4) of 1.5 mg/ml chymotrypsin. Cells were also incubated continuously with 1.5 mg/ml chymotrypsin during a 15-min preincubation in methionine-free DME, a 15-min pulse with 35S-Translabel™, and a 15-min chase (A, lane 2). Alternatively, cells were pulsed for 15 min and chased for 1 h at 37°C. The cells were then shifted to 4°C, and incubated an additional 45 min in the presence of 1.5 mg/ml chymotrypsin (A, lane 5, marked with asterisk). For each labeling scheme, AE1 immunoprecipitates were prepared from total cell lysates using a polyclonal antibody directed against the cytoplasmic domain of AE1-4. A fraction of the total cell lysate was also analyzed by immunoblotting using a polyclonal antibody that recognizes α-fodrin (A) or a chicken AE1-specific peptide antibody (A). Additional studies examined the effect of various reagents on the posttranslational processing of AE1-4. MDCK cells stably expressing AE1-4 were pulsed with 35S-Translabel™ for 15 min, and chased for 1 h (B, lane 1), or 4 h (B, lanes 2–5). For some of the cells, 25 mM ammonium chloride (A, lane 3), 10 μg/ml BFA (B, lane 4), or 0.4 M sucrose (B, lane 5) was added to media after 45 min of chase, and was present for the remainder of the chase period. At each time point, AE1 immunoprecipitates were prepared from total cell lysates. Immunoprecipitates in A and B were analyzed on a 6% SDS polyacrylamide gel, and labeled anion exchangers were detected by fluorography.
