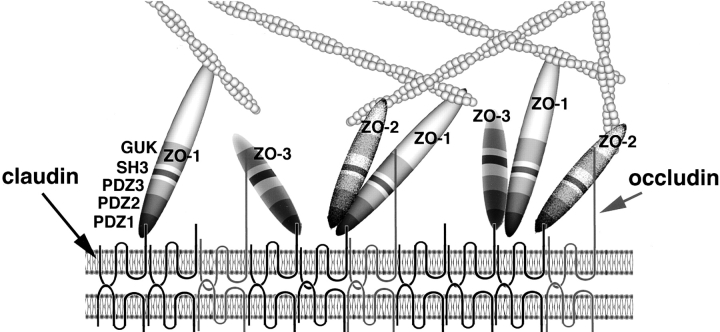
Figure 11.
Schematic drawing of the molecular architecture of the TJ plaque. TJ strands are represented as linear co-polymers of claudins and occludin with short and long COOH-terminal tails, respectively. ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3 are directly associated with the COOH termini of claudins at their PDZ1 domains. These molecules are depicted here to interact with occludin at their GUK domains. ZO-1/ZO-2 and ZO-1/ZO-3 heterodimers are depicted to be formed through direct PDZ2/PDZ2 interaction, but the possibility cannot be completely excluded that these interaction requires some linker protein. It remains unclear whether ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3 exist as monomers and/or homodimers (not depicted here), except that ZO-1/ZO-1 homodimers were reported to be undetectable. The COOH-terminal region of ZO-1 and ZO-2 has a binding affinity to actin filaments to function as cross-linkers between TJ strands and actin filaments. The interaction between ZO-3 and actin filaments has not yet been examined.