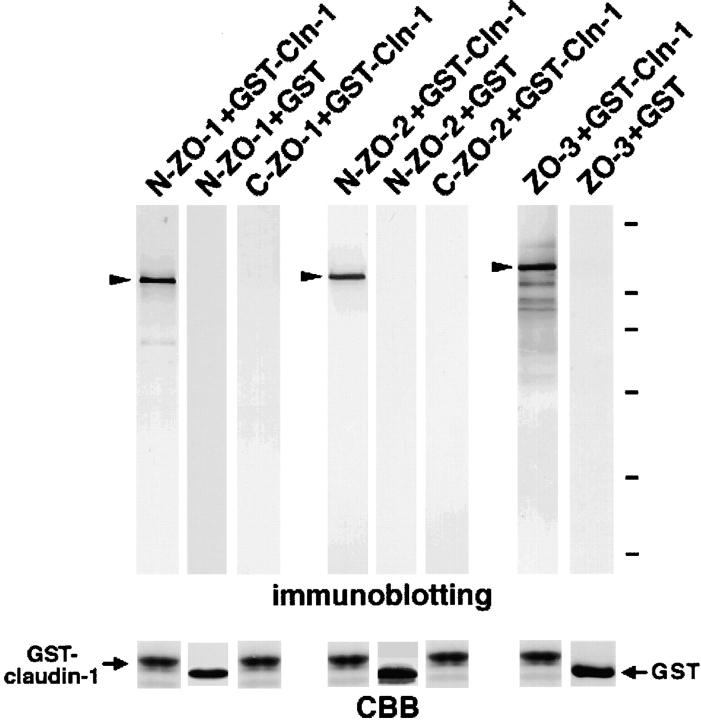
Figure 3.
Association of N-ZO-1, N-ZO-2, and full-length ZO-3 with the cytoplasmic domain of claudin-1 in vitro. The GST fusion protein with the cytoplasmic domain of claudin-1 (GST-Cln-1) or GST protein (GST), which was bound to glutathione–Sepharose beads, was incubated with the lysate of Sf9 cells expressing N-ZO-1, C-ZO-1, 6xHis-N-ZO-2, or 6xHis-C-ZO-2, or with the lysate of E. coli expressing 6xHis-tagged full-length ZO-3. In each lysate, the amount of recombinant protein was adjusted to be the same. After washing, the proteins associated with GST fusion protein or GST were eluted from the beads with a buffer containing glutathione. The eluates from N-ZO-1–, C-ZO-1–, 6xHis-N-ZO-2–, 6xHis-C-ZO-2–, or 6xHis-ZO-3–incubated beads were separated by SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting with anti–ZO-1 mAb T8754, anti–ZO-1 mAb T7713, anti-His tag mAb, anti-His tag mAb, or anti-His tag mAb (immunoblotting). The amount of GST–claudin-1 (GST-claudin-1) and GST (GST) in each eluate was determined by Coomassie brilliant blue staining (CBB). As indicated by arrowheads, N-ZO-1, N-ZO-2, full-length ZO-3, but not C-ZO-1 or C-ZO-2, showed binding affinity to the cytoplasmic domain of claudin-1. Bars indicate molecular masses of 200, 116, 97, 66, 45, and 31 kD, respectively, from the top.