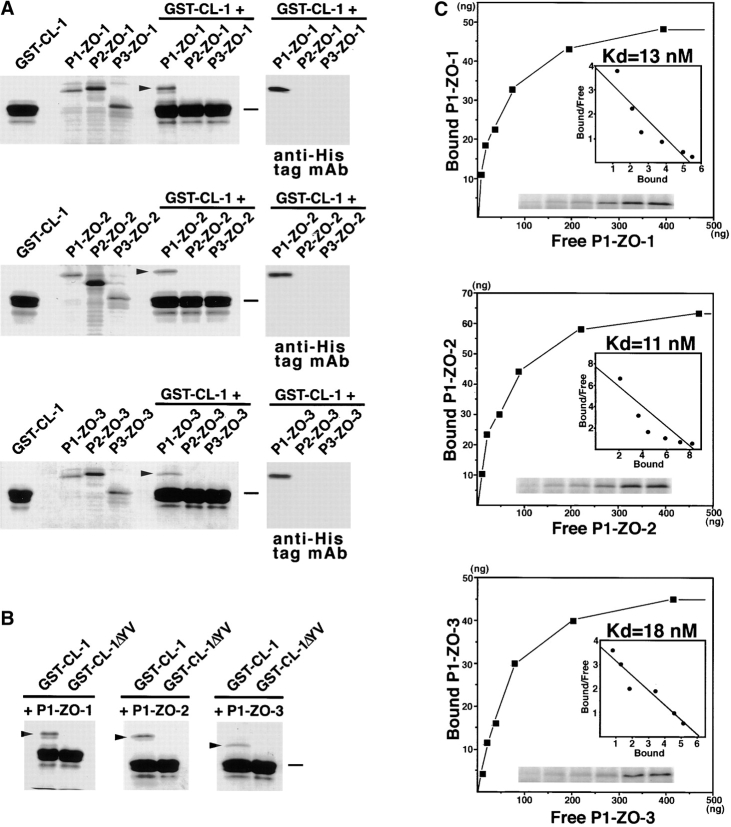
Figure 4.
Association of PDZ1 domains of ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3 with the COOH-terminal YV sequence of claudin-1. All SDS-PAGE gels were stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. (A) The GST fusion protein with the cytoplasmic domain of claudin-1 (GST-CL-1), which was bound to glutathione–Sepharose beads, was incubated with the lysate of E. coli expressing 6xHis-PDZ1 domains (P1-ZO-1, P1-ZO-2, P1-ZO-3), 6xHis-PDZ2 domains (P2-ZO-1, P2-ZO-2, P2-ZO-3), and 6xHis-PDZ3 domains (P3-ZO-1, P3-ZO-2, P3-ZO-3) of ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3. After washing, the proteins associated with GST fusion proteins were eluted from the beads with a buffer containing glutathione. The eluates from PDZ domain-incubated beads were separated by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie brilliant blue staining or by immunoblotting with anti-His tag mAb (anti-His tag mAb). Among the 9 PDZ domains, only P1-ZO-1, P1-ZO-2, and P1-ZO-3 were associated with the cytoplasmic domain of claudin-1 (arrowheads). (B) Similar binding assay was performed between P1-ZO-1/P1-ZO-2/P1-ZO-3 and GST fusion protein with the COOH-terminal YV-deleted cytoplasmic domain of claudin-1 (GST-CL-1ΔYV). P1-ZO-1, P1-ZO-2, and P1-ZO-3 bound to GST-CL-1 (arrowheads), but not to GST-CL-1ΔYV. Bars indicate a molecular mass of 31 kD. (C) Quantitative analysis of the binding between PDZ1 domains of ZO-1/ZO-2/ZO-3 and the cytoplasmic domain of claudin-1. Glutathione–Sepharose bead slurry containing GST-claudin-1 was incubated with E. coli lysate containing 0.01–0.5 μg of the PDZ1 domain of ZO-1, ZO-2, or ZO-3 (from the top). The amounts of the PDZ1 domain of ZO-1, ZO-2, or ZO-3 in the E. coli lysate and in each eluate (inset) were estimated as described in Materials and Methods. Each point represents the mean value of triplicate determinations. The binding was saturable, and Scatchard analysis (inset) indicated that the K d values for the PDZ1 domains of ZO-1 (P1-ZO-1), ZO-2 (P1-ZO-2), and ZO-3 (P1-ZO-3) were ∼13, 11, and 18 nM, respectively.