Figure 8.
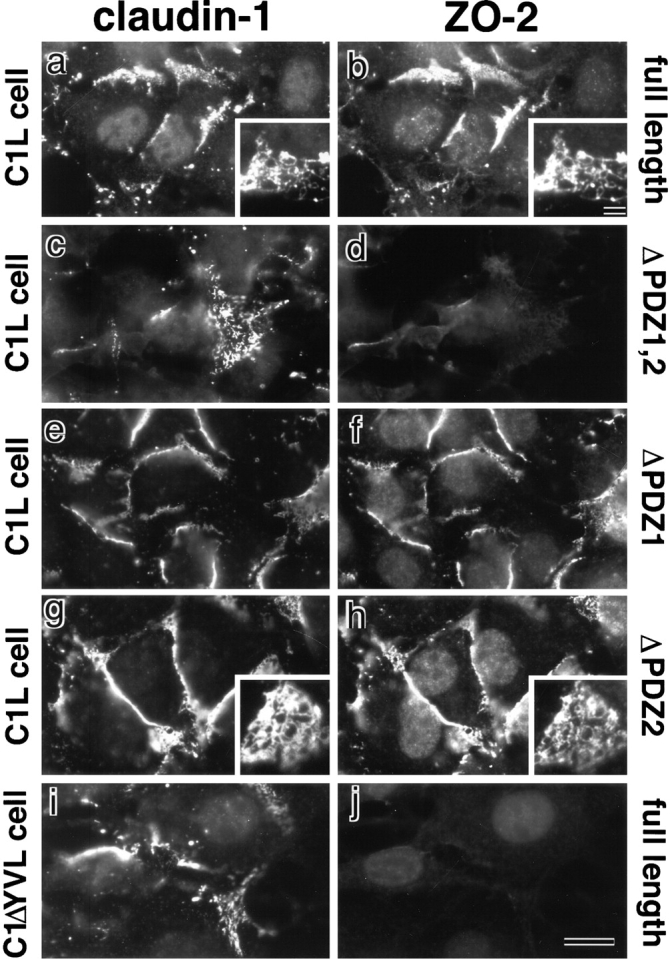
Recruitment of exogenous ZO-2 to claudin-based networks in L transfectants expressing claudin-1. Full-length ZO-2 (full-length; a and b), deletion mutant of ZO-2 lacking both PDZ1 and -2 domains (ΔPDZ1,2; c and d), deletion mutant of ZO-2 lacking PDZ1 domain (ΔPDZ1; e and f), and deletion mutant of ZO-2 lacking PDZ2 domain (ΔPDZ2; g and h) were transfected into L transfectants expressing claudin-1 (C1L cells), and stable transfectants were obtained. Furthermore, full-length ZO-2 (full-length; i and j) was transfected into L transfectants expressing claudin-1 mutant lacking its COOH-terminal YV sequence (C1ΔYVL cell), and stable transfectants were obtained. These introduced proteins were tagged with c-myc epitope. These stable transfectants were double stained with anti–claudin-1 mAb (a, c, e, and g) or pAb (i) and anti–c-myc mAb (b, d, f, h, and j). In C1L cells where claudin-1 was concentrated at cell–cell borders in an elaborate network pattern, full-length ZO-2 (b), ΔPDZ1-ZO-2 (f), and ΔPDZ2-ZO-2 (h), but not ΔPDZ1,2-ZO-2 (d), were recruited to the claudin-1–based networks. Insets represent the network patterns of concentrated claudin-1 (a and g), full-length ZO-2 (b), and ΔPDZ2-ZO-2 (h). No concentration of full-length ZO-2 was observed in C1ΔYVL cells (j). Bar: (a–j) 10 μm; (insets) 15 μm.
